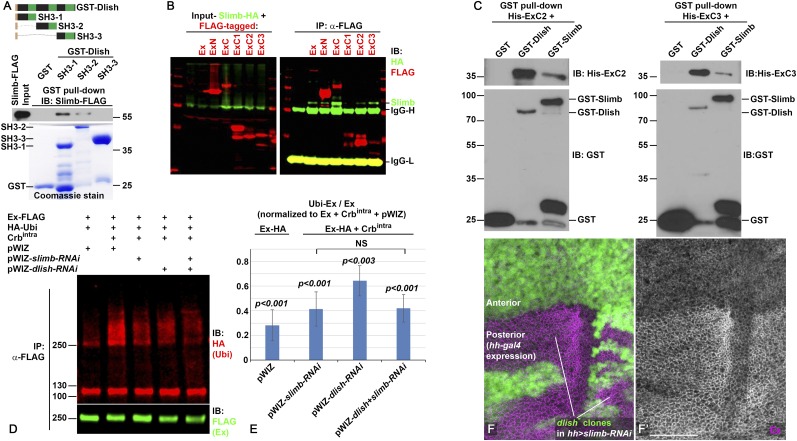
Fig. 6.
Dlish binds Slimb and regulates Ex ubiquitination. (A) Slimb-FLAG from S2R+ cells is pulled down by GST-Dlish-SH3-1 and GST-Dlish-SH3-2 but not by GST-Dlish-SH3-3. (B) FLAG-tagged Ex, ExN, ExC, ExC2, and ExC3 co-IP with Slimb-HA in S2R+ cells. (C) His-ExC2 and His-ExC3 purified from Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) are pulled down by GST-Dlish and GST-Slimb. (D and E) RNAi-mediated depletion of Dlish or Slimb in S2R+ cells reduces Crbintra-stimulated ubiquitination of Ex. (D) Example Western IB of ubiquitination assay; Ubi, ubiqutin. (E) Quantification of five ubiquitination assays. Ratios of ubiquitinated Ex (Ubi-Ex) to total Ex on each IB were normalized to the control Ex-FLAG + Crbintra condition (=1.0). Changes were compared with the control using paired two-tailed t tests; NS, not significant. Error bars show ±SD. (F) The increased subapical Ex (magenta, gray in F′) in the posterior of hh-gal4 UAS-slimb-RNAi wing discs is not affected by homozygous dlish4506 clones (loss of green). (Scale bar: 50 μm.)