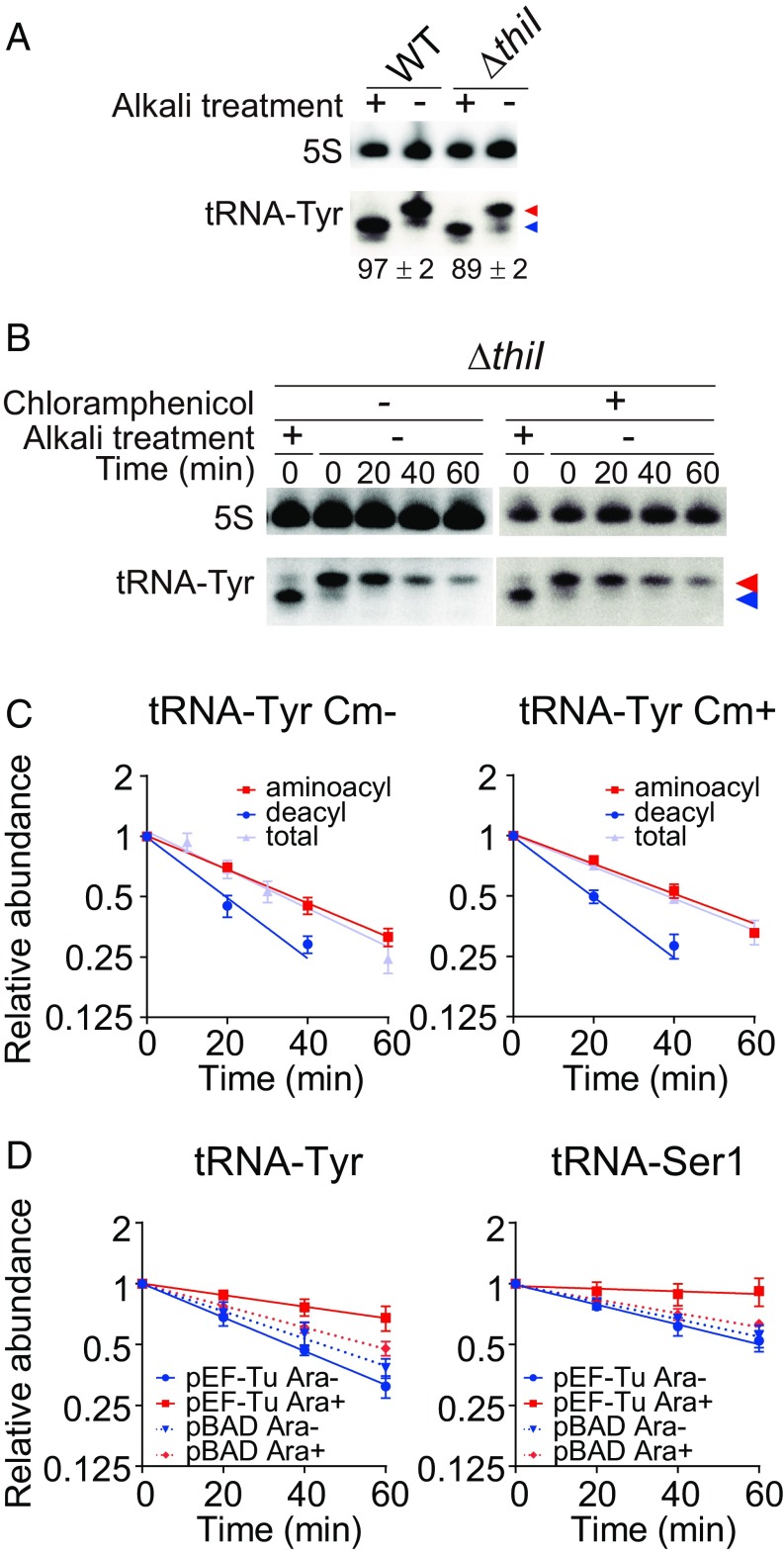
Fig. 6.
EF-Tu protects aminoacyl-tRNAs from RNA degradosome-mediated decay. (A) Aminoacylation levels of tRNA-Tyr in WT and ΔthiI strains. Total RNAs from early stationary phase (1 h after OD600) were resolved on 6.5% acid gels and analyzed by Northern blotting. Means ± SD of aminoacylation level from three independent experiments are shown. Red and blue arrowheads indicate aminoacylated and deacylated tRNAs, respectively. (B and C) Decay of aminoacylated and deacylated tRNAs in early stationary-phase cultures after rifampicin treatment. Total RNAs were resolved on 6.5% acid gels and analyzed by Northern blotting with or without chloramphenicol (Cm) (B); decay curves of the lower band (deacylated tRNA), upper band (aminoacylated tRNA), and total tRNA-Tyr (calculated from neutral PAGE Northern blotting analysis) are shown in C. Red and blue arrowheads in B indicate aminoacylated and deacylated tRNAs, respectively. (D) Decay curves of tRNA-Tyr and tRNA-Ser1 from the ΔthiI strain containing a vector encoding arabinose-inducible EF-Tu (pEF-Tu) or an empty vector (pBAD) with or without 0.2% arabinose.