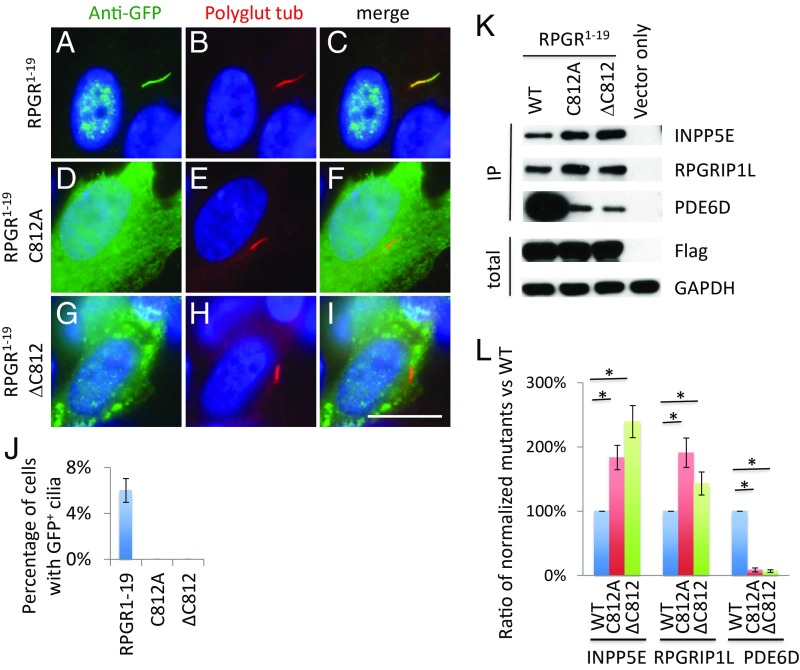
Fig. 2.
Prenylation of the C terminus of RPGR1−19 regulates its interaction with endogenous PDE6D, INPP5E, and RPGRIP1L. The C terminus of RPGR1−19 contains a cysteine residue for prenylation. Mutation (D–F) or deletion (G–I) of the cysteine residue abolish the ability of the RPGR1−19 isoform to localize to cilia compared with WT control (A–C). (J) Quantification of percentage of cells with GFP+ cilia in transfected RPE1 cells. (K) Disruption of RPGR prenylation affects its interaction with endogenous PDE6D, INPP5E, and RPGRIP1L. Flag-S-tag–conjugated WT and mutant RPGR1−19 were transfected into HEK293T cells, and RPGR was pulled down by Flag beads. Western blots were used to detect RPGR1−19 interaction proteins using antibodies against PDE6D, INPP5E, and RPGRIP1L. (L) The ratio of mutants to WT was calculated after quantifying each band using ImageJ and normalized to Flag and GAPDH. Each transfection was done three times. *P < 0.05. (Scale bar: 10 μm.)