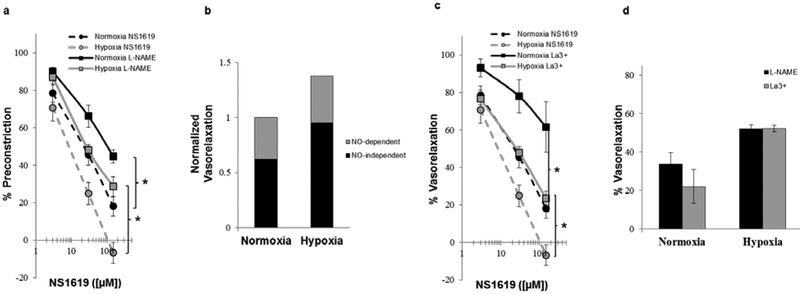
Fig. 4.
Concentration-response relation of isolated perfused lungs from normoxic and hypoxic rats (n = 4–6/group) to NS1619 in the absence (vehicle) and presence of (a) L-NAME (100 μM; nitric oxide synthase inhibitor) and (c) lanthanum (La3+; 100 μM; non-specific cation/TRP channel blocker). Qualitative representation of the relative contribution of NO-dependent and NO-independent mechanisms to vasorelaxation (b). Comparison of the resultant percent vasorelaxation, in response to NS1619 ([30μM]), of normoxic and hypoxic lungs in the presence of L-NAME and La3+ (d). Values are means ± SE. *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle within same condition