Figure 1.
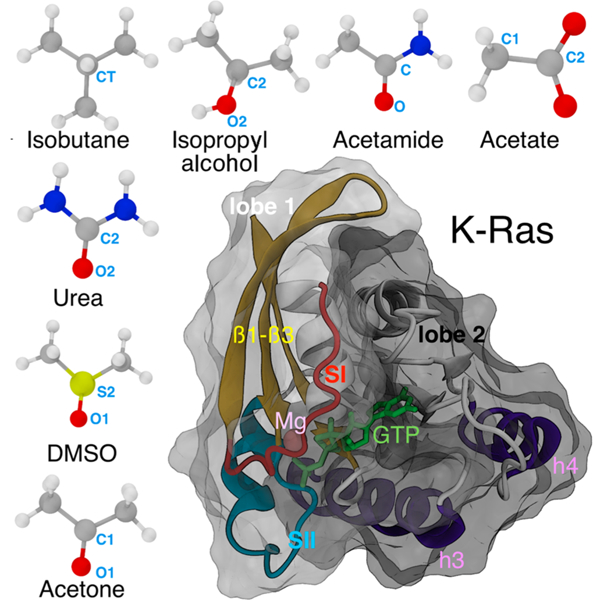
Structure of K-Ras and the small organic probe molecules used in this study. A CPK representation of isobutane, isopropyl alcohol, acetamide, acetate, acetone, DMSO, and urea with carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and hydrogen atoms in gray, red, blue, yellow, and white, respectively. The central labeled atoms (C, C1, C2, CT, and S2) are used for modification of LJ potentials (see Table 1), and the peripheral labeled atoms (any of the terminal carbons in the case of isobutane) are used to define orientation vectors (see Methods). The catalytic domain structure of G12D K-Ras (PDB id: 4DSO) is shown in cartoon with lobe 1 (residues 1–86) and lobe 2 (residues 87–166) highlighted as surface overlays in light gray and black, respectively. The bound GTP (sticks) and Mg (sphere) are also highlighted.
