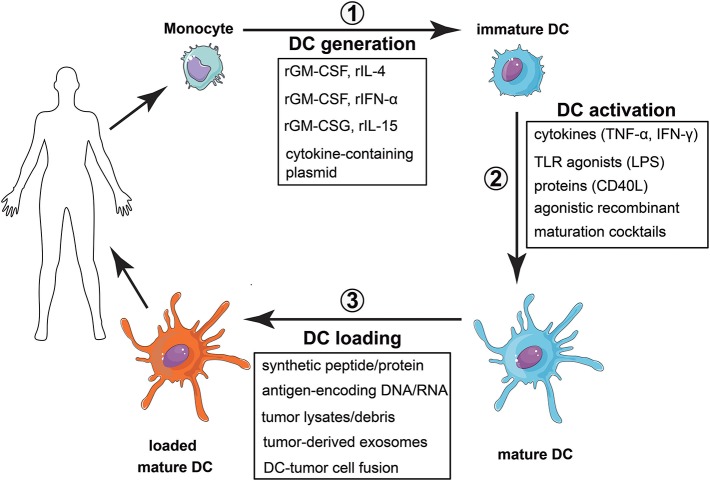
Figure 5.
Vaccination strategy with monocyte derived dendritic cells. (1) Monocytes are obtained from peripheral blood and differentiated into dendritic cells. This differentiation can be achieved by using different recombinant cytokines, with rGMCSF + rIL-4 as the most common combination, or by transfecting monocytes with plasmids encoding the cytokines. (2) Once differentiated, DC activation can be accomplished by using different stimuli, most of them associated with tissue damage, inflammation or the presence of a pathogen. (3) The last step is to load the DC with selected or total tumor antigens. Finally, the cells are injected in the patient, expecting them to induce a tumor-specific adaptive immune response able to eradicate the tumor.