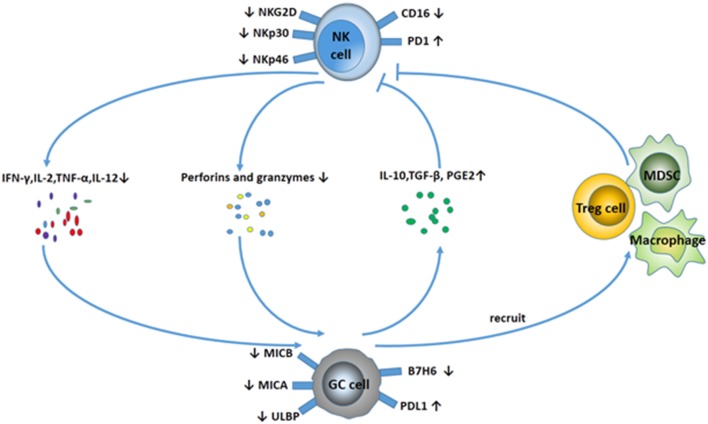
Figure 2.
Interaction between NK cells and GC. NK cells display a suppressive phenotype with fewer activating receptors (NKG2D, NKp30, NKp46) and higher expression of PD-1 in GC patients. In addition, NK cells secret fewer cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-2, TNF-α, IL-12), and the ability to release perforins and granzymes is decreased. Meanwhile, GC cells downregulate the expression of MICA/B, ULBP, and B7H6 to avoid NK cell-mediated innate immunity. GC cells can also release some cytokines, including IL-10, TGF-β, and PGE2, and recruit MDSCs and Treg cells to suppress NK cell activity.