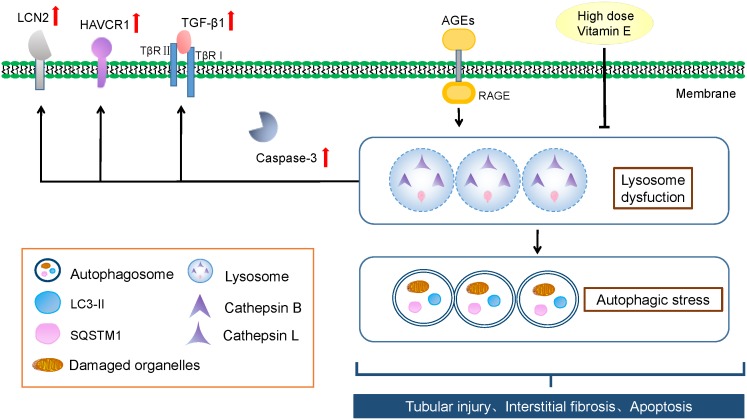
FIGURE 9.
Schematic representation of vitamin E’s renoprotective effect and the autophagic stress-associated mechanisms. AGEs induces autophagic stress by blocking lysosomal-dependent degradation of autophagosomes in proximal tubules in DN, irrespective of autophagosome formation. And the accumulation of autophagic vacuoles and autophagy substrate is likely a sign of increased autophagic stress. High dose vitamin E could attenuate TEC injury and prevent the progression of DN by depressing autophagic stress.