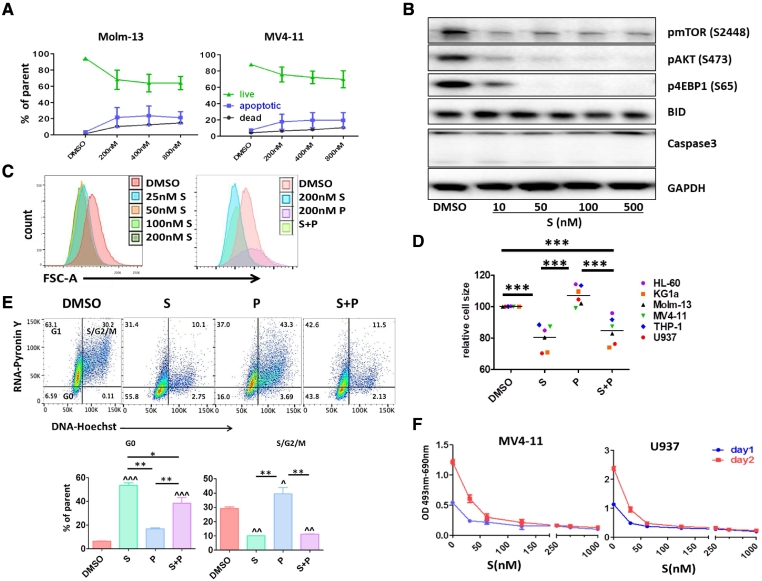
Figure 4.
S led AML cells into a dormant/ quiescent status. A. Annexin V and 7AAD apoptosis flow cytometry analysis shows that S did not significantly induce cell death. Molm-13 and MV4–11 cells were treated with different concentrations of S for 48 hours and the percentage of live, apoptotic and dead cell was determined by flow cytometry. B. U937 cells were treated with different concentrations of S for 48 hours and western blot analysis was performed. C. Molm-13 cells were treated with different concentrations of S or S and P combination for 1 day followed by flow cytometry cell size analysis. Representative flow cytometry figures show that S sharply shifted FSC to the left at the concentration as low as 25 nM. D. S significantly reduced AML cell size. After 1 day of exposure, AML cell size was determined using FSC-A parameter by flow cytometry (***P < .001) in the presence of S, P, or S + P. E. S remarkably arrested AML cells in G0-phase. After 24 hours 200 nM P or S alone or combination treatment, RNA/DNA levels were analyzed using pyronin Y (RNA) and Hoechst (DNA) staining following by flow cytometry. ^P < .05, ^^P < .01, ^^^P < .001 compared to vehicle DMSO control; *P < .05, **P < .01 using one-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls Multiple Comparison Test. F. MV4–11 and U937 cells were treated with different concentrations of S for 1 or 2 days, cell metabolic activity was measured by XTT assay.