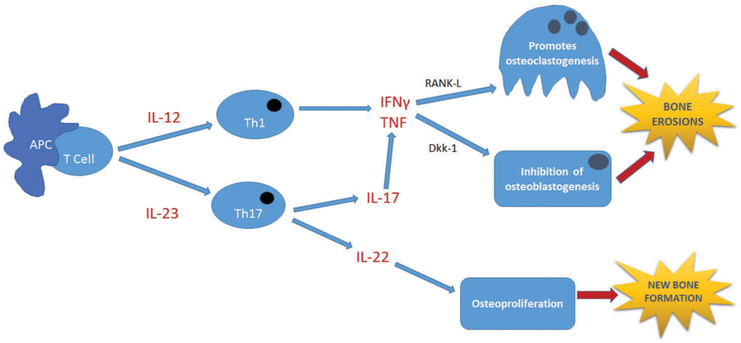
Figure 3.
Pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis.
The Th1 and Th17 pathways are important pathways involved in the pathogenesis of PsA. TNF, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, is a key player in osteoclastogenesis via RANK-L and in inhibition of osteoblastogenesis via Dkk-1. Both processes eventually lead to bone erosions [42]. In addition, IL-22 is involved in the pathologic formation of new bone (osteoproliferation) [43]. APC, antigen presenting cell; Dkk-1, dickkopf-related protein 1; IFNγ, interferon gamma; IL-12, interleukin-12; IL-17, interleukin-17; IL-22, interleukin-22; IL-23, interleukin-23; RANK-L, receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand; T cell, T lymphocyte; Th1, type 1 T helper cell; Th17, T helper 17 cell; TNF, tumor necrosis factor