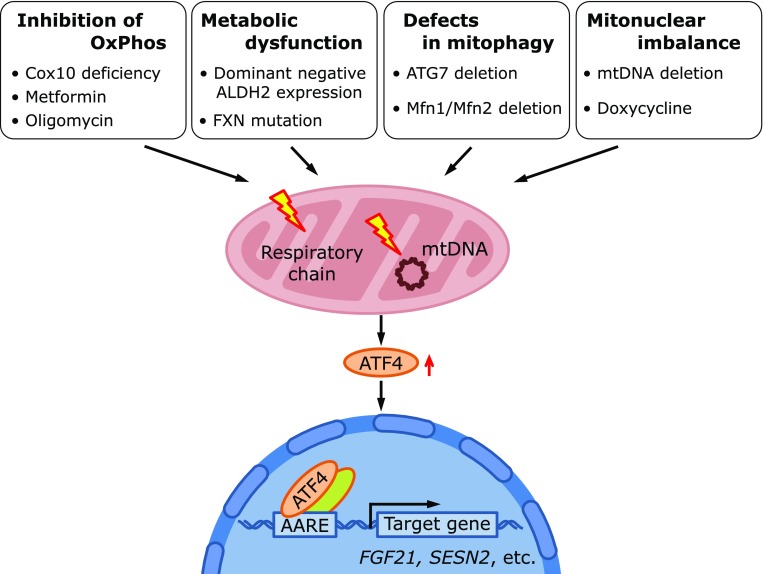
Fig. 3.
ATF4 is activated by the perturbation of mitochondrial function. Perturbation of mitochondrial function induces ATF4 activation. Genetic alteration or inhibition of OxPhos enzymes increases ROS production, which may induce ATF4 activation. ATF4 is also activated by the dysregulation of other metabolic pathways, such as reactive aldehyde accumulation by dominant negative ALDH2 expression or perturbed iron homeostasis by FXN deficiency. Mitophagy regulates mitochondrial quality control by eliminating damaged, depolarized mitochondria. Defects in mitophagy induce the accumulation of impaired mitochondria and ATF4 activation. An imbalance in mitochondrial- and nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins caused by mtDNA deletion or mitochondrial ribosome inhibition by doxycycline confers ATF4 activation. FXN, frataxin; OxPhos, oxidative phosphorylation.