Fig. 4.
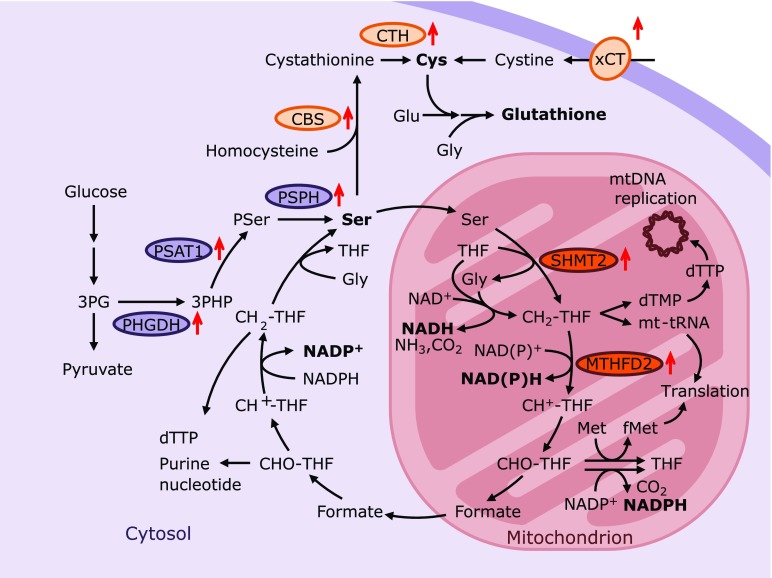
ATF4 regulates the serine synthetic and mitochondrial Folate-mediated 1C metabolism pathway. Several ATF4 target genes are involved in serine synthesis, 1C unit metabolism, purine synthesis and glutathione synthesis. The expression of PHGDH, PSAT1 and PSPH increases serine synthesis. Serine is incorporated into glutathione synthesis as well as into 1C unit metabolism. Expression of xCT, CTH and CBS increases glutathione synthesis. The expression of SHMT2 and MTHFD2 accelerates NADPH production, fMet synthesis and purine synthesis, which are important for mitochondrial redox homeostasis, mitochondrial translation and DNA replication, respectively. SHMT2-mediated tRNA methylation is important for the translation of mitochondria-encoded electrophile transport chain. In proliferating cells, CHO-THF and CH2-THF generated in the cytosol is utilized for purine and thymidine synthesis, respectively. 3PG, 3-phospho-glycerate; 3PHP, 3-phospho-hydroxypyruvate; CBS, cystathionine-β-synthase; CH2-THF, 5,10-methylene-THF; CH+-THF, 5,10-methenyl-THF; CHO-THF, 10-formyl-THF; CTH, cystathionase; dTMP, thymidine monophosphate; dTTP, thymidine triphosphate; fMet, N-formylmethionine; MTHFD2, methylene-tetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2; PHGDH, phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; PSAT1, phosphoserine aminotransferase 1; PSer, 3-phospho-serine; PSPH, phosphoserine phosphatase; SHMT2, mitochondrial serine hydroxymethyl transferase 2; THF, tetrahydrofolate.