Figure 3.
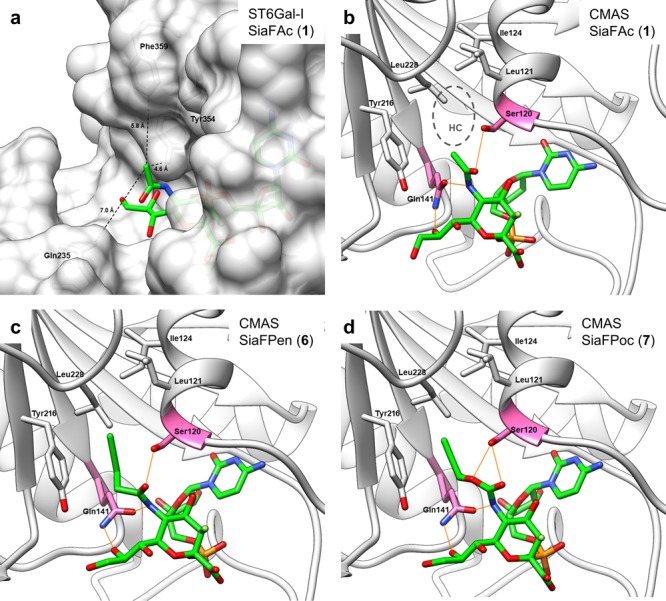
(a) CMP–SiaFAc (from 5BO9, green carbons) was superposed onto cocrystalized CMP in the ST6Gal-I binding pocket (4JS2, white carbons and surface). Distances (Å) to nearest residues Gln235, Tyr354, and Phe359 are indicated with black dashes. (b) Cocrystalized CMP–Sia (green carbons) in the CMAS binding pocket (1QWJ, domain D, white carbons). Between the HC (Leu121, Ile124, Tyr216, and Leu228) and the sialic acid pyranose ring, there is a hydrophilic gate (Ser120, Gln141, pink carbons). Hydrogen bonds are depicted with orange lines. (c,d) Energy-minimized poses of SiaFPen (6) [green carbons, (c)] and SiaFPoc (7) [green carbons, (d)] in the CMAS binding pocket (1QWJ, domain D, white carbons). Hydrogen bonds are depicted with orange lines. The hydrophilic gate accommodates the carbamate [SiaFPoc, (d)] more favorably than the amide [SiaFPen, (c)] because of an additional polar interaction with Ser120.
