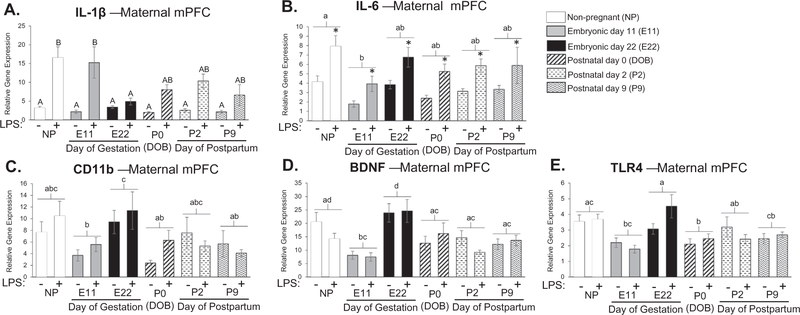
Fig. 4.
Examination of cytokine expression in maternal medial prefrontal cortex at various time-points throughout pregnancy and the postpartum period. There was a treatment by condition interaction for IL-1β gene expression (F5,80 = 2.668; p = 0.028) where LPS-induced IL-1β expression was significantly attenuated at E22 compared to non-pregnant controls (E22: p = 0.002; A). There was a main effect of condition and treatment for IL-6 gene expression where E11 pregnancy time-point was significantly different than non-pregnant controls (Condition: F5,78 = 2.550; p = 0.034, Treatment: F1,78 = 26.209; p < 0.001; B). There was also a main effect of condition for CD11b where E11, P0, and P9 were significantly different than non-pregnant controls (F5,79 = 3.144; p = 0.012; C). We found a main effect of condition for BDNF where E11 expression is significantly decreased compared to the non-pregnant group and that E22 is significantly increased compared to all other time-points with the exception of the non-pregnant group (F5,79 = 8.451; p = < 0.001; D). There was a main effect in TLR4 expression where P0 was significantly suppressed compared to the non-pregnant group, and E22 gene expression was significantly higher in E11, P0, and P9 (F5,80 = 5.608; p = < 0.001; E). n = 7–8 rats per group. Condition × Treatment interaction: groups that do not share any capital letters are considered significantly significant (p < 0.05). Main effect of Condition: groups that do not share any lowercase letters are considered statistically significant (p < 0.05). Main effect of Treatment: groups with an asterisk are considered statistically significant (p < 0.05).