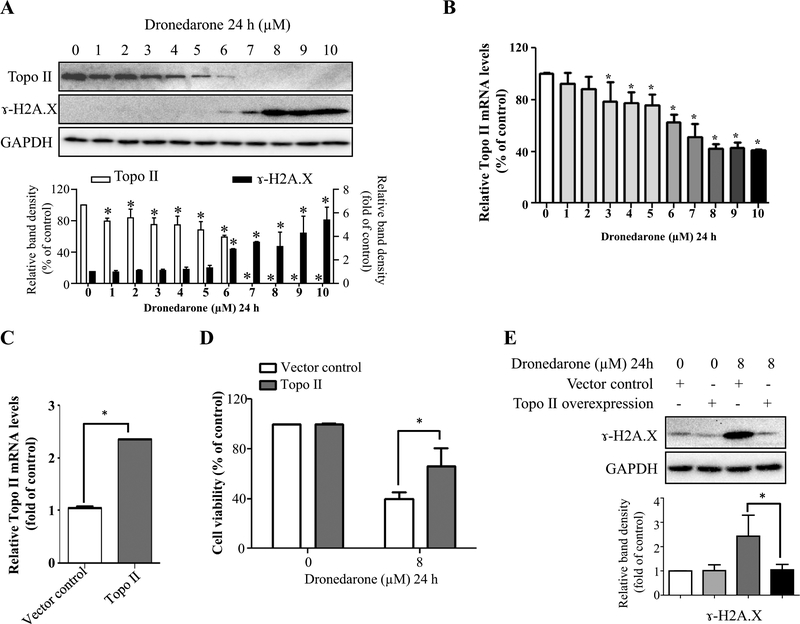
Fig. 6.
Suppressed topoisomerase II levels contribute to dronedarone-induced DNA damage in HepG2 cells. a Total cellular proteins were extracted after dronedarone treatment at indicated concentrations for 24 h. The levels of topoisomerase II and γ-H2A.X were measured by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. Intensities of bands were normalized to the amount of GAPDH. *p < 0.05 versus treatment of DMSO vehicle control. b Total RNA were extracted after dronedarone treatment at indicated concentrations for 24 h. c HepG2 cells were infected with lentivirus carrying topoisomerase II. The gene expression level of topoisomerase II was measured by real-time PCR. Human GAPDH was used as an internal control to normalize the amount of cDNA template. The results shown are mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 compared with DMSO control (b) or vector control (c). d, e Empty vector or topoisomerase II transduced HepG2 cells were treated with 8 μM dronedarone for 24 h. d Cytotoxicity was measured using MTS assay. *p < 0.05 compared with vector control. e The expression level of γ-H2A.X was detected by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. Intensities of bands were normalized to the amount of GAPDH. *p < 0.05 compared with vector control