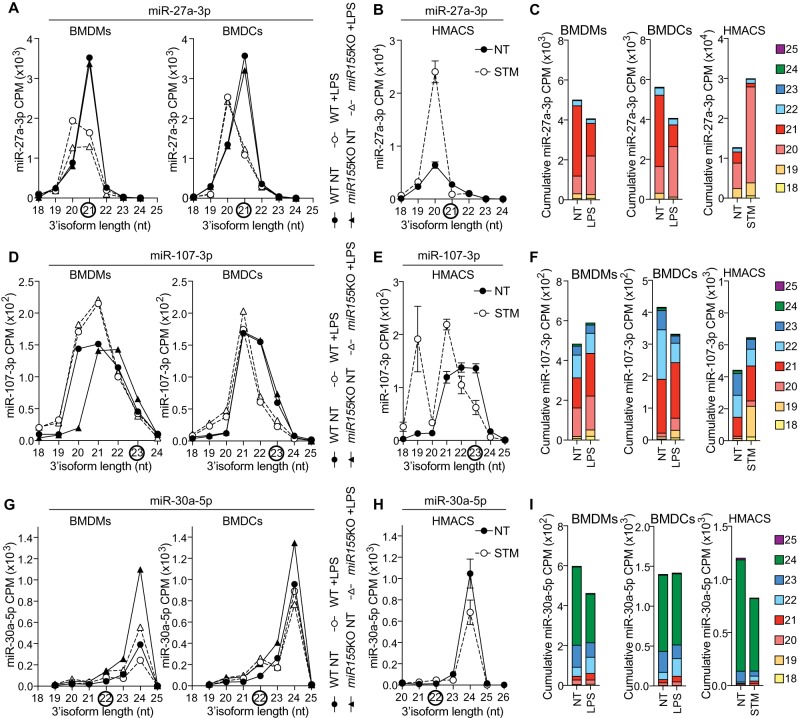
FIGURE 3.
Bacterial-driven modulation of miR-27a-3p, miR-107-3p, and miR-30a-5p isoforms in human and mouse macrophages. (A,D,G) Detailed analysis of CPM for the 3′-end isoforms of miR-27a-3p (A), miR-107-3p (D), and miR-30a-5p (G) in BMDMs and BMDCs from wild-type (WT) and miR-155-deficient mice (Dueck et al. 2014). Data shown are from one biological sample for each condition. Black circles highlight miRBase canonical isoforms. (B,E,H) Detailed analysis of CPM for the 3′-end isoforms of miR-27a-3p (B), miR-107-3p (E), and miR-30a-5p (H) in human monocyte-derived macrophages, infected for 24 h with Salmonella Typhimurium (STM) at an MOI of 5:1, compared to NT cells at 24 h (Pai et al. 2016). Data are averaged from six patients (mean ± standard error of the mean is shown). Black circles highlight miRBase canonical isoforms. (C,F,I) CPM of the prevalent miR-27a-3p (C), miR-107-3p (F), and miR-30a-5p (I) 3′-end isoforms from NT and LPS-treated WT BMDMs/BMDCs and STM-infected human macrophages were cumulated to reflect the overall impact of bacterial products on the pool of miRNA molecules.