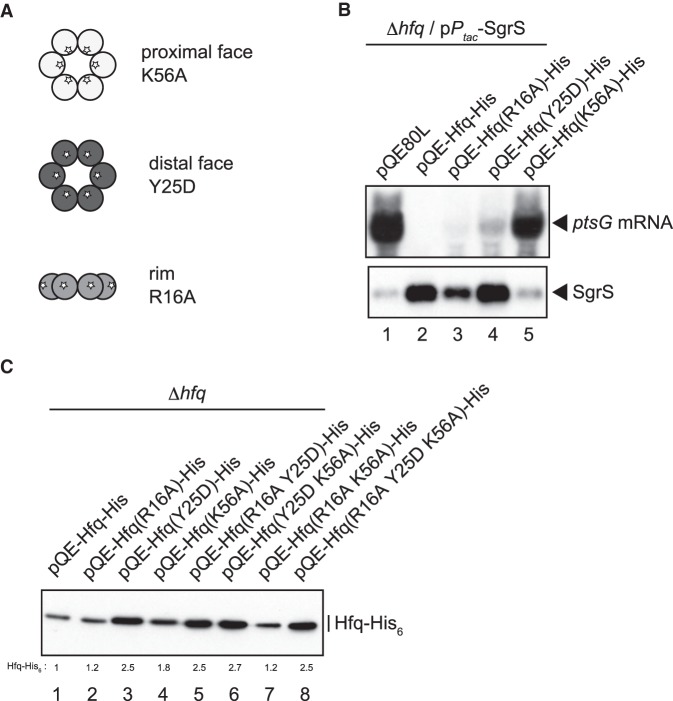
FIGURE 2.
(A) A schematic drawing of the Hfq hexamer and location of three representative mutations on RNA-binding surfaces. (B) Properties of the Hfq-His6 derivatives carrying mutations in RNA-binding surfaces. TM589 (Δhfq) cells harboring indicated plasmids were grown in LB medium containing 50 µM IPTG to A600 = ∼0.6 and total RNAs were prepared. Ten micrograms or 1 µg of RNA samples was subjected to northern blotting using ptsG probe or SgrS probe, respectively. (C) Effects of mutations of RNA-binding surfaces on Hfq-His6 expression. Overnight cultures of TM589 (Δhfq) cells harboring indicated plasmids were inoculated (1/100-fold) into LB medium containing 1 mM IPTG. Incubation was continued for 90 min and then total proteins were prepared. Protein samples equivalent to 0.0125 A600 units were subjected to western blotting using anti-His6 monoclonal antibody. Relative levels of Hfq-His6 derivatives are calculated, with the pQE-Hfq-His sample set to one.