Figure 1.
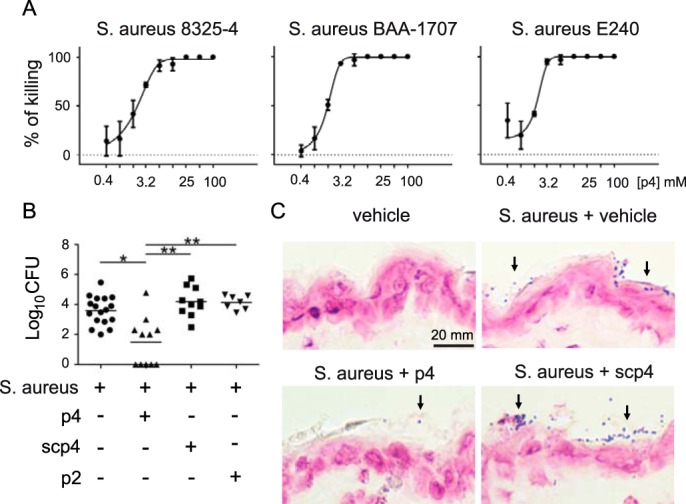
Chemerin-derived p4 peptide is bactericidal in vitro and in vivo. A, the indicated S. aureus strains were incubated with p4 for 24 h. Data show the percentage of killing for the indicated strain. The MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of p4 showing no visible growth (100% of killing). Mean ± S.D. of three independent measurements is shown. B, mice were topically infected with 1 × 107 cfu of S. aureus 8325-4 in the presence of 100 μm peptide p4, scp4, p2, or vehicle. Data points indicate the colony-forming units of bacteria recovered from the skin surface 24 h after application of bacteria, with each data point representing one cavity and a horizontal line indicating the mean value in each group; n = 5 independent experiments. **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05 by Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Dunn's multiple comparisons test. C, mice were topically treated with vehicle or infected with 1 × 107 cfu S. aureus 8325-4 in the presence of 100 μm peptide p4, scp4, or vehicle for 24 h. Gram-positive S. aureus on the skin surface is indicated by arrows. Data are from one experiment and are representative of three independent experiments.
