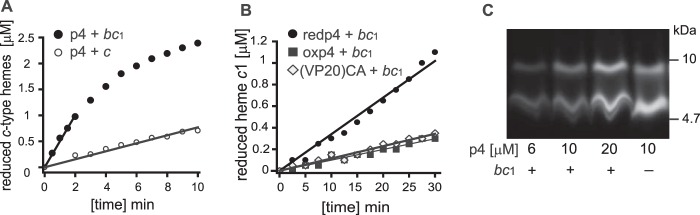
Figure 7.
p4 and/or redp4 are able to reduce cytochrome c1 or cytochrome c and form dimers in the presence of cytochrome bc1. A, comparison of the ability of p4 to reduce cytochrome c1 of cytochrome bc1 (black) and cytochrome c (white). The concentrations of cytochromes and p4 were 6 μm and 60 μm, respectively. Cytochrome bc1 was fully oxidized by ferricyanide prior addition of p4. Cytochrome c was almost fully oxidized prior addition of p4. Conditions were 50 mm Tris (pH 8.0), 100 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, and 0.01% n-dodecyl-d-maltoside. Measured data points were fitted to the linear function. All linear coefficients of determination (R2) were above 0.95. B, reduction of cytochrome c1 of cytochrome bc1 in the presence of redp4 (black circles), oxp4 (black rectangles), or the (VP20)CA variant (white diamonds). The concentration of cytochrome bc1 and peptides was 6 μm. Cytochrome bc1 was fully oxidized by ferricyanide prior addition of peptides. C, the indicated concentrations of FITC-p4 were incubated with 6 μm cytochrome bc1 for 10 min as described in A. p4 was then analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by gel imaging.