Figure 2.
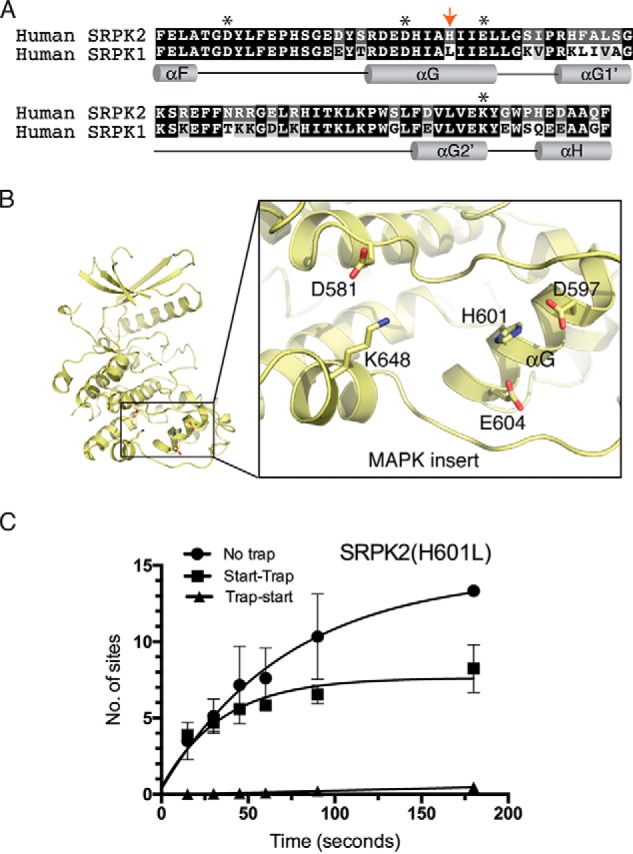
His-601 is responsible for the lower processivity observed in SRPK2. A, alignment and comparison of the amino acid sequences of SRPK2 and SRPK1 docking grooves. Docking groove residues critical for substrate binding and phosphorylation mechanism are denoted by asterisks. His-601 of SRPK2 is denoted by a red arrow. B, His-601 of the helix αG is positioned at the center of the docking groove. C, phosphorylation of SRSF1 by SRPK2(H601L) under no trap, trap-start, and start-trap conditions. The number of phosphorylation sites on SRSF1 has increased to 7.8 ± 0.5 (Fig. 1D). Error bars, S.D. from three independent experiments.
