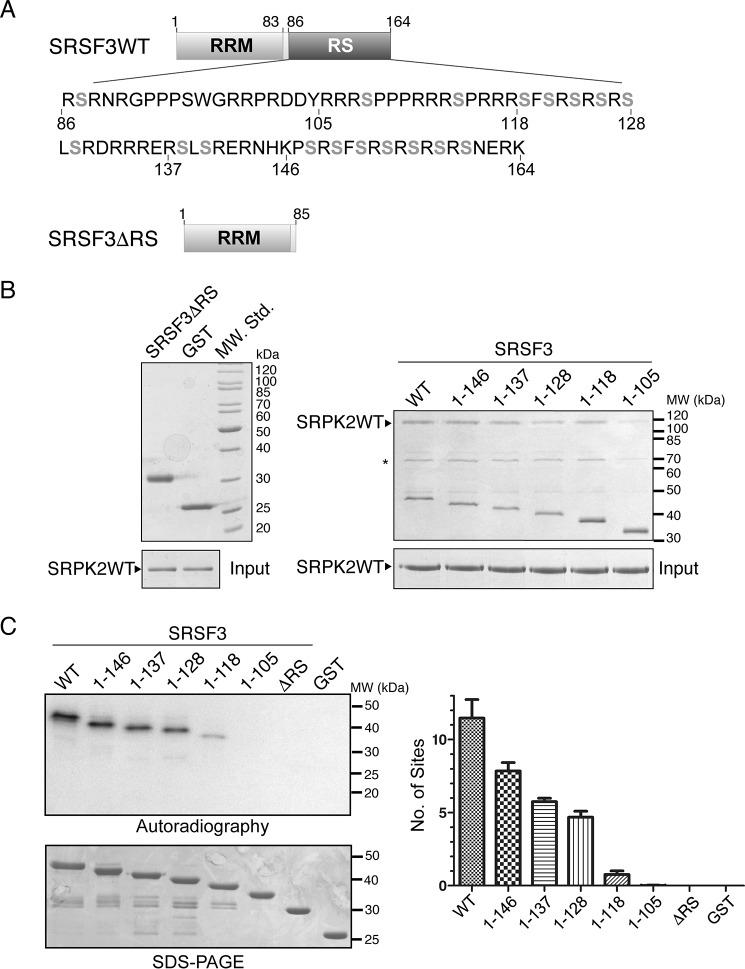
Figure 4.
RS domain of SRSF3 is important for interaction with SRPK2. A, domain organizations of SRSF3WT and SRSF3ΔRS (aa 1–85) are shown. 18 potentially phosphorylatable serines that are present in the context of either RS or SR dipeptides are denoted in gray boldface type. B, GST pulldown assay samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained by Coomassie Blue. Deletion of the RS domain of GST-tagged SRSF3 completely abolished its interaction with SRPK2 (left). GST-tagged SRSF3(1–105) failed to bind SRPK2 with similar efficiency as other C-terminally truncated constructs, indicating that residues C-terminal to aa 105 are critical for the interaction. Asterisks denote minor impurity bands. C, RS/SR dipeptides C-terminal to aa 105 were phosphorylated by SRPK2. WT or mutant SRSF3 (500 nm) was phosphorylated by SRPK2 (1.5 μm) using 100 μm [32P]ATP until the end point was reached (15 min). Radiolabeled protein bands corresponding to the phosphorylated SRSF3 constructs were excised and quantified by scintillation counting. Error bars, S.D.