Figure 6.
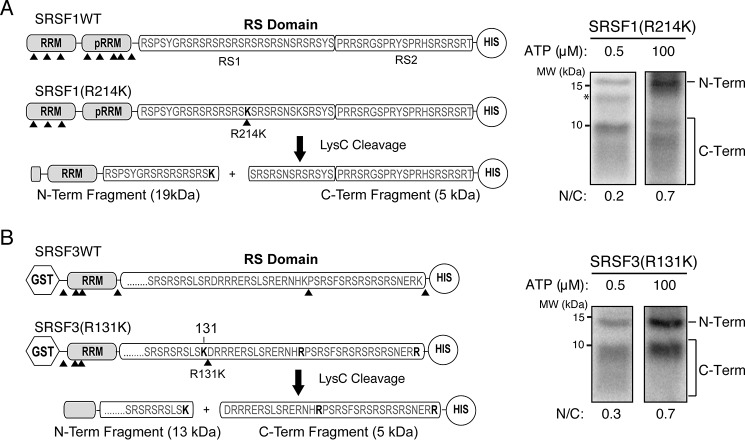
Both SRSF1 and SRSF3 are phosphorylated at the C-terminal region first. A, left, cleavage construct of SRSF1. Positions of lysine are denoted by arrowheads. The C-terminal His-tagged SRSF1(R214K) construct contains five Lys-to-Arg mutations in the RRM2 and a single Arg-to-Lys mutation at position 214 of the RS domain. Cleavage of the construct by Lys-C produces two major N-terminal and C-terminal fragments of 19 and 5 kDa, respectively. Asterisk, minor impurity band. Right, Lys-C cleavage of SRPK2-phosphorylated SRSF1(R214K) at 0.5 μm (low) and 100 μm (high) ATP concentrations. The autoradiogram was scanned, and the ratio of N-terminal band to C-terminal fragments (N/C) was determined by a PhosphorImager. B, left, cleavage construct of SRSF3. The C-terminal His-tagged SRSF3(R131K) construct contains three Lys-to-Arg mutations and a single Arg-to-Lys mutation at position 131 of the RS domain. Lys-C cleavage produces two major N-terminal and C-terminal fragments of 13 and 4 kDa, respectively. Right, Lys-C cleavage of SRPK2-phosphorylated SRSF3(R131K) at low and high ATP concentrations.