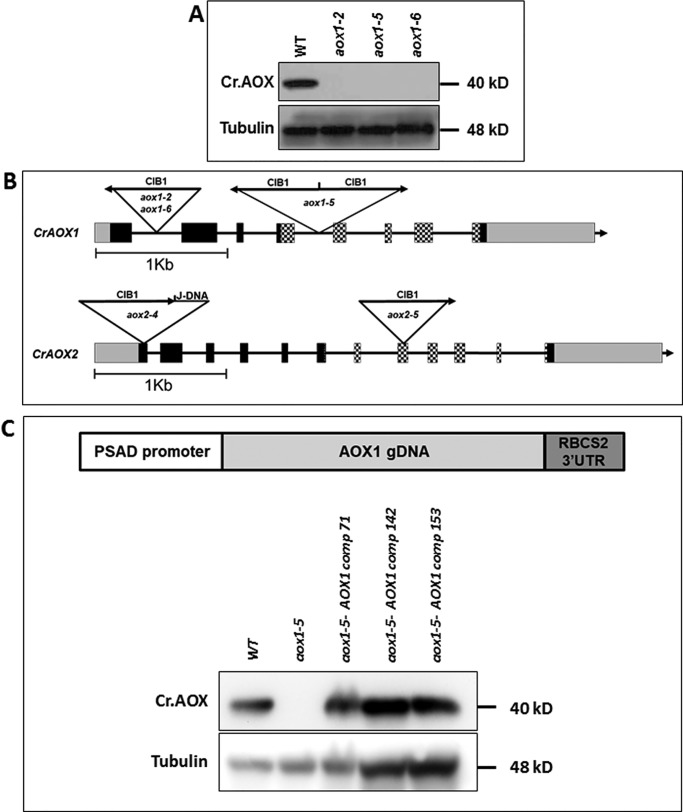
Figure 2.
Insertions in aox mutants and their inability to synthesize AOX1 protein. A, immunoblots blot showing CrAOX1 protein in WT cells and the aox1-2, aox1-5, and aox1-6 mutants. AOX1 protein accumulation was assayed under mixotrophic, HL conditions. Tubulin was used as a loading control. Molecular masses of proteins are given to the right of the gel image. B, positions of CIB1 insertions in the CrAOX1 and CrAOX2 genes of aox1-2, aox1-5, aox1-6, aox2-4, and aox2-5 mutants. Arrows indicate the orientation of the insertions. The boxes and lines are defined in the legend to Fig. 1. C (top), general construct used to complement the aox1 mutant (pRam118-gAOX1-RBCS2 3′-UTR; see Fig. S6). Bottom, immunoblots showing CrAOX1 accumulation in WT cells (CMJ30), aox1, and three complemented strains (colonies 71, 142, and 153). AOX1 accumulation was assayed under mixotrophic, HL conditions. The tubulin protein was used as a loading control. Molecular masses of the proteins are given to the right of the gel image.