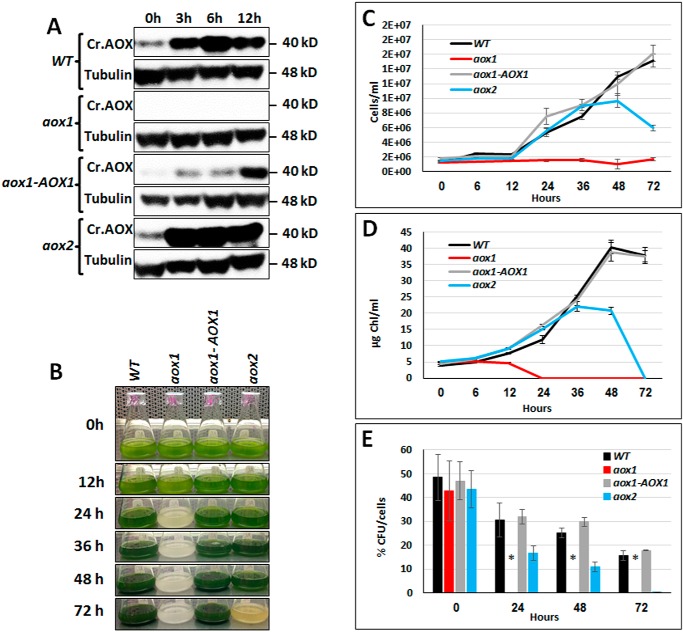
Figure 3.
Accumulation of AOX1 protein in aox1 and aox2 mutants and their survival in high light. A, immunoblots showing CrAOX protein accumulation in C. reinhardtii WT, aox1, aox2, and the aox1-AOX1 rescued strain exposed to HL (1,200 μmol of photons m−2 s−1) following growth in 60 μmol of photons m−2 s−1. Samples were collected 3, 6, and 12 h after being exposed to HL, and the polypeptides in the samples resolved by SDS-PAGE and CrAOX1 were quantified by immunodetection using a monospecific antibody. CrAOX1 accumulation (top panels) was normalized to the level of tubulin (loading control); detection of tubulin was with a monospecific antibody. Molecular masses of the proteins are to the right of the image. B, image showing cultures of various strains (as indicated) in TAP medium, under HL conditions for various times, and up to 3 days (72 h). C, growth of the various strains (as indicated) in TAP medium, based on cell number, following exposure to HL for various times, and up to 3 days (72 h). D, chlorophyll levels in the cultures after exposure to HL for various times and up to 3 days. Data for the growth experiments (C and D) are based on three biological replicates (performed at the same time); error bars, S.D. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. E, survival (cfu/cell) of WT, aox1, the aox1-AOX1 rescued strains, and aox2. Samples were exposed to HL (1,200 μmol of photons m−2 s−1) for the indicated times (0–72 h) and were then plated onto solid TAP medium (1.5% agar plates) and grown in LL until colonies were observed (10 days). Student's t test was performed (*, significant difference (p < 0.05)). All results presented were derived from samples of cultures exposed to HL (1,200 μmol of photons m−2 s−1) for the indicated period.