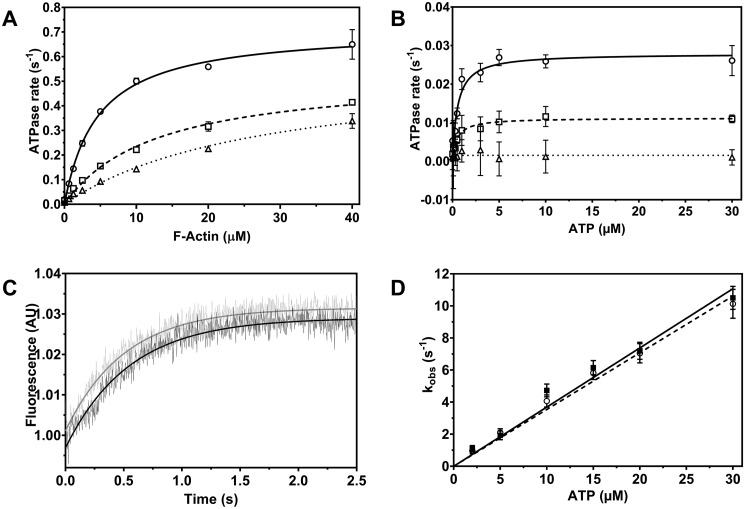
Figure 4.
Phenamacril-induced changes in myosin function. A, actin-activated ATPase activity of FgMyo1 was measured over the range from 0 to 40 μm F-actin in the absence and presence of phenamacril. Open circle, ethanol control (0 μm phenamacril) (kcat,actin = 0.72 ± 0.04 s−1, Kapp,actin = 4.80 ± 0.5 μm); open square, 300 nm (kcat,actin = 0.51 ± 0.03 s−1, Kapp,actin = 11.7 ± 0.09 μm); open triangle, 600 nm phenamacril (kcat,actin = 0.49 ± 0.05 s−1, Kapp,actin = 24.9 ± 3.5 μm). B, basal ATPase activity of FgMyo1 was measured in assay buffer containing Ca2+ and ATP in the range from 0 to 30 μm. Open circle, ethanol control (0 μm phenamacril): kcat,basal = 0.028 ± 0.0009 s−1, Kapp,basal = 0.60 ± 0.09 μm); open square, 600 nm phenamacril: kcat,basal = 0.011 ± 0.0004 s−1, Kapp,basal = 0.53 ± 0.09 μm); open triangle, 10 μm phenamacril: no ATP turnover. C, inhibition of ATP-induced dissociation of the acto-FgMyo1-MD complex are monitored by the associated change in pyrene-actin fluorescence. The transients shown were obtained after mixing a complex of 0.4 μm FgMyo1-MD and 0.2 μm pyrene-actin with 10 μm ATP in the presence of 2% ethanol (control, black transient) or 10 μm phenamacril (gray transient). The rate constants (kobs) for the dissociation of the actomyosin complex are obtained from exponential fits to the data and correspond to 1.93 s−1 (control) and 2.11 s−1 (10 μm phenamacril). Traces were normalized to their starting values. D, the kobs values of the ATP-induced dissociation plotted against a series of ATP concentrations in the absence (control, filled square) and presence (open circle) of 10 μm phenamacril (in both syringes) are shown as a linear fit to the data. The apparent second-order rate constant (K1k+2) for ATP binding to acto-FgMyo1 is 0.37 ± 0.02 μm−1s−1 in the absence and 0.35 ± 0.01 μm−1s−1 in the presence of phenamacril. Data in panels A and B were fitted by the hyperbolic Michaelis-Menten function. Error bars denote the S.D. around the mean (A and B: n = 4 reactions, two replicate series; D: n = 4–6 measurements, two independent experiments).