Figure 5.
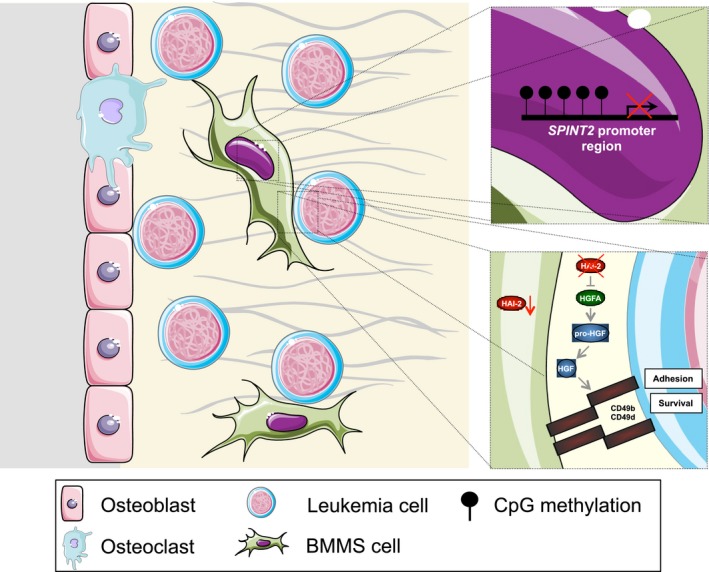
Schematic pathway hypothesis of the biological effects of SPINT2/HAI‐2 in haematological neoplasms (Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Acute Myeloid Leukemia, AML). Methylation results in the inhibition of SPINT2/HAI‐2 expression in bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells from myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and de novo AML patients, resulting in increased secretion of HGF with consequent increase in cell adhesion and in survival/growth of hematopoietic cells, mainly of the abnormal MDS and de novo AML cells, and contributing with the functional abnormalities of microenvironment niche and with cancer progression. This figure was created using Servier Medical Art tools (http://www.servier.com)
