Figure 4.
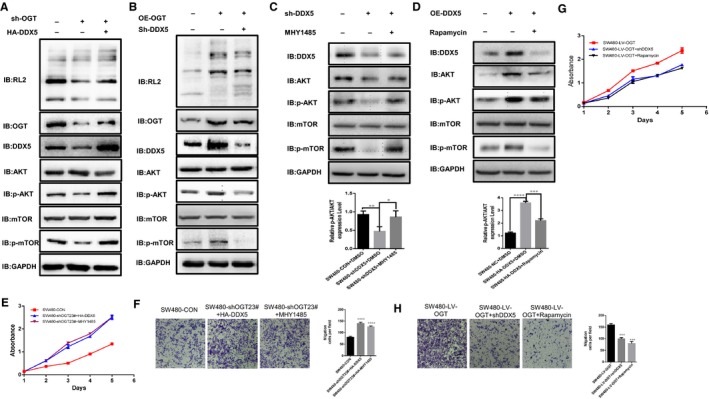
OGT‐DDX5 axis affects colon cancer proliferation and metastasis by regulating AKT/mTOR pathway. A, B, C, and D, The levels of O‐GlcNAcylation, OGT, DDX5, AKT, p‐AKT, mTOR, and p‐mTOR were detected by WB. A, WB detects the activation level of the AKT/mTOR signalling pathway after knockdown of OGT or overexpression of DDX5. B, WB detects the level of activation of the AKT/mTOR signalling pathway after overexpression of OGT or knockdown of DDX5. C, WB detects the activation level of the AKT/mTOR signalling pathway after knockdown DDX5 or adding MHY1485. D, WB detects the activation level of the AKT/mTOR signalling pathway after overexpressing DDX5 or adding Rapamycin. E, F, G, and H. The aberrantly activated AKT/mTOR signalling pathway rescued a reduction in the transformed phenotype caused by OGT knockdown in vitro. Representative images from three independent experiments are shown (A‐E). **P < 0.01 indicates statistical significance. The data from E‐H were analysed by one‐way and two‐way ANOVA, respectively
