Figure 2.
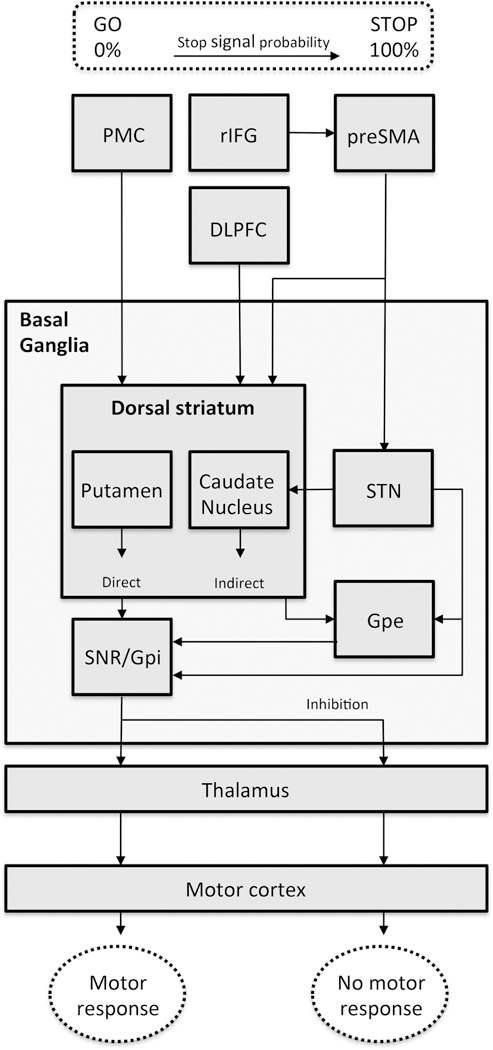
A simplified schematic overview of the neurobiological aspects of reactive and proactive response inhibition. In this model we included the rIFG as attentional monitor and suggest influence of the rIFG on the preSMA during increasing stop signal probability. We propose a main role of the preSMA for both reactive and proactive inhibition. The squared boxes indicate brain areas and the dotted lines indicate observable features and the basal ganglia and striatum. Abbreviations: PMC = premotor cortex, rIFG = right inferior frontal gyrus, DLPFC = dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, preSMA = presupplementary motor area, SNr = substantia nigra pars reticulate, GPi = internal segments of the globus pallidus, GPe = external segments of the globus pallidus, SNc = substantia nigra pars compacta, STN = subthalamic nucleus.
