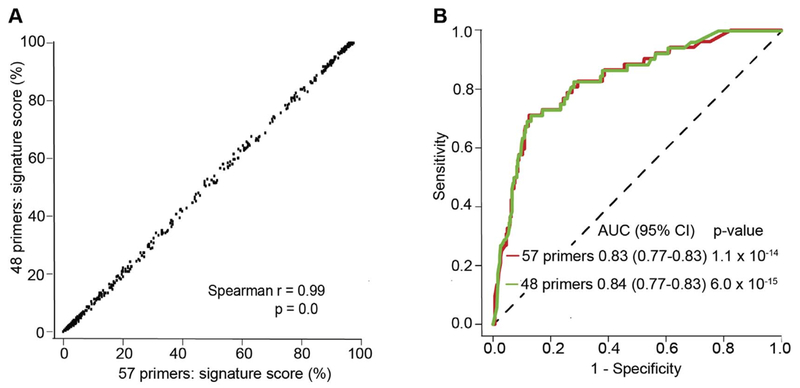
Figure 3. Performance of the reduced ACS 11-gene signature of TB risk as a classifier of TB disease from M.tb-infection in PBMC.
(A) Correlation of the signature scores generated from the original 57 primer-probe (16 genes) and the reduced, 48 primer-probe (11-genes) qRT-PCR transcriptomic signatures of risk of TB disease in progressors and controls from the Adolescent Cohort Study (ACS). The Spearman correlation coefficient is shown. (B) Performance of the original and reduced CoR signatures in classifying progressor and control samples from the Adolescent Cohort Study. In Darboe F, Mbandi SK, Thompson EG, Fisher M, Rodo M, van Rooyen M, Filander E, Bilek N, Mabwe S, Hatherill M, Zak DE, Penn-Nicholson A, Scriba TJ, SATVI Clinical Immunology Team. Diagnostic performance of an optimized transcriptomic signature of risk of tuberculosis in cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Tuberculosis 2018; 108:124–126. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2017.11.001.