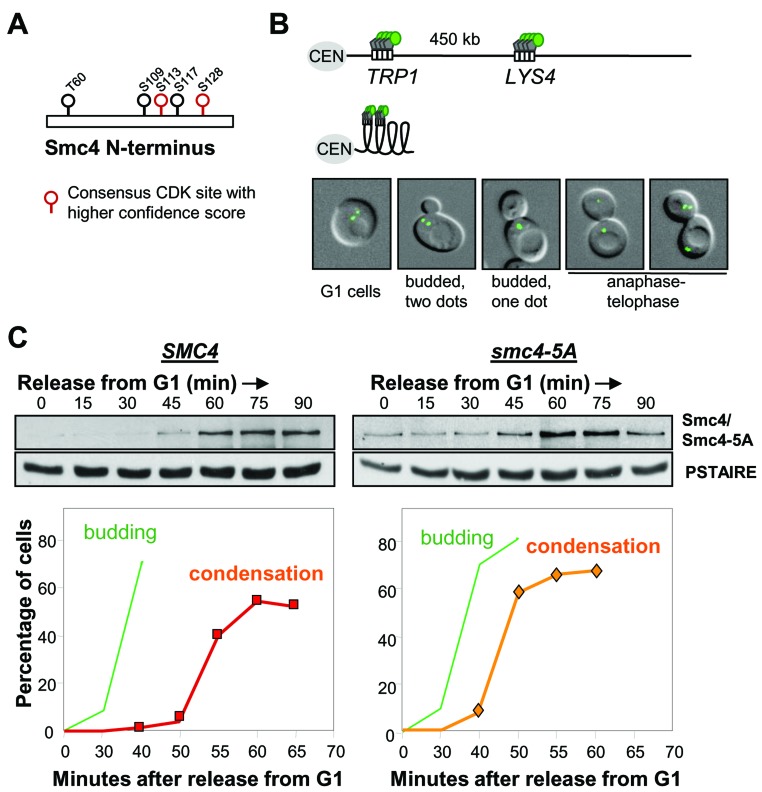
Figure 1. Smc4 CDK sites are dispensable for chromosome condensation.
A. Cdk full consensus sequences in S. cerevisiae Smc4. Solid circles indicate residues known to be phosphorylated; determined by proteome-wide analysis (see text). Residues with higher confidence scores are shown in red. B. Cartoon showing the LacO/GFP-LacI system used for the condensation assay. Two-separated GFP signals can be detected on uncondensed right arm of chromosome IV (Top). Condensed chromosome IV brings two GFP signals together (Bottom). White rectangle indicates Lac operator sequence. Gray pentagon indicates Lac repressor protein. Green circle indicates green fluorescence protein. CEN: centromere. The images are wild type yeast cells with GFP marked TRP1 and LYS4 loci in various stages of the cell cycle. From left to right: G1 (unbudded with two GFP dots), S (Small bud with 2 GFP dots), G2/M (budded with one GFP dot, indicating chromosome condensation) and Anaphase/Telophase (one or 2 GFP dots in each daughter cell). C. Analysis of a synchronous cell cycle after G1 arrest (mating pheromone) in wild type and smc4-5A cells. After releasing from G1 arrest, samples were taken for scoring budding (green) and chromosome condensation (red/orange). The Western blots show wild type Smc4 and Smc4-5A protein levels. PSTAIRE is the loading control.