Figure 3.
Several Prevalent Intestinal uSGBs Are Found within the Clostridiales Order Related to Ruminococcus and Faecalibacterium
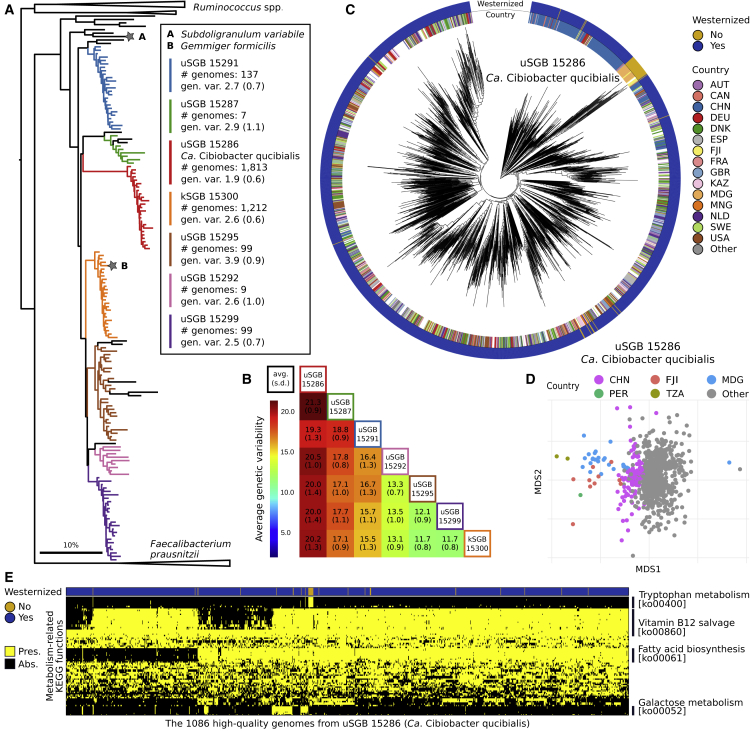
(A) All SGBs in the assembled phylogeny (Figure 1A) placed between reference genomes for Ruminococcus and Faecalibacterium species that are reported as collapsed trees. A maximum of 25 HQ genomes from each SGB are displayed, and SGBs with <3 genomes are left black.
(B) The monophyletic clade with the six uSGBs and the kSGB containing Gemmiger formicilis represent clearly divergent species with inter-species genetic distance typical of genus-level divergence (average 16.6%, SD 3.1% nucleotide distance).
(C) A whole-genome phylogeny for the 1,806 genomes in Ca. Cibiobacter qucibialis (STAR Methods). Some subtrees associate with geography and non-Westernized populations, while others seems to be geography- and lifestyle-independent (see text).
(D) Multidimensional scaling of genetic distances among genomes of Ca. Cibiobacter qucibialis highlights the divergence of strains carried by non-Westernized populations, with Chinese populations subclustering within the large cluster of Westernized populations.
(E) Madagascar-associated strains of Ca. Cibiobacter qucibialis (uSGB 15286) uniquely possess the trp operon for tryptophan metabolism (Table S7). Other functional clusters in Westernized strains from geographically heterogeneous populations include vitamin B12 and fatty acid biosynthesis and galactose metabolism. The KEGG functions present in >80% or in <20% of the samples were discarded except for significant associations with lifestyle.