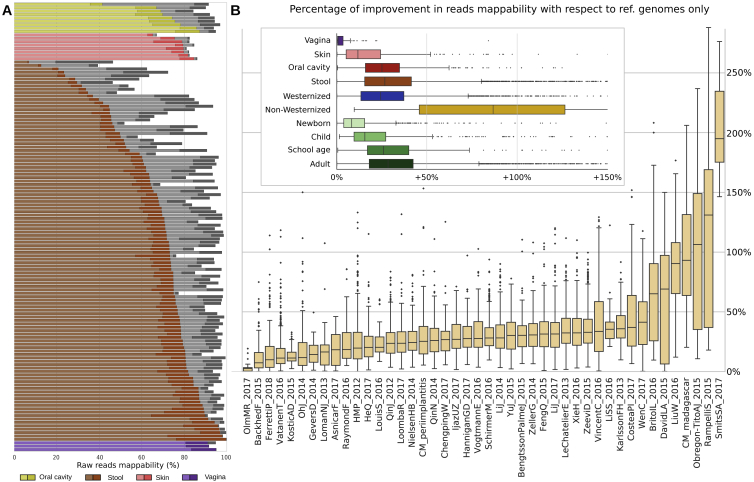
Figure S4.
Improvement of Read Mappability Statistics by Considering the Set of Microbial Genomes We Assembled in This Work, Related to Figure 2
(A) Fraction of reads that can be mapped against different sets of genomes from isolate sequencing and the metagenomically reconstructed genomes. A subset of 132 full (i.e., not subsampled) metagenomes is shown (3 metagenomes randomly selected from each study). Samples are colored and grouped by body site. The colored part of the bar refers to the reads that can be mapped against a previously available reference genome, while the gray bars extend to highlight the total mappability we achieved using the 154,723 microbial genomes reconstructed in this study. (B) Percentage of increase in the mappability when using also the 154,723 reconstructed SGBs to map metagenomic reads. Boxplots represent values grouped by body site, lifestyle, age category (upper panel) and study (lower panel). The percentage of improvement is calculated with respect to the fraction of reads that could map using only and all the reference genomes. All the 9,428 metagenomes used in this study were mapped after being subsampled at 1% (see STAR Methods). Averaged statistics are reported in Figures 2A–2B.