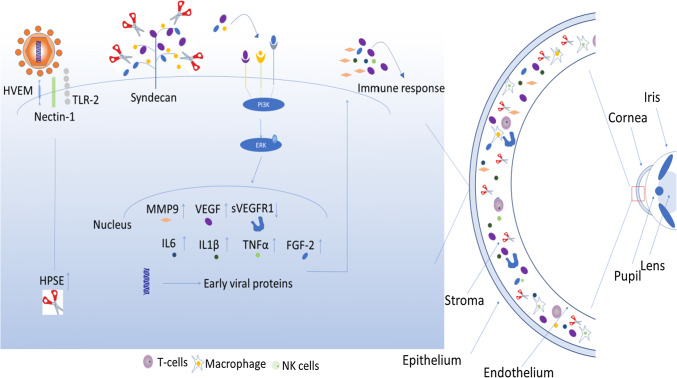
Fig. 4.
Induction of corneal neovascularization and inflammation by HSV-1 infection: HSV-1 infection results in the increased expression of heparanase (HPSE) which causes heparan sulfate proteoglycan (e.g., syndecan) shedding. HPSE-degraded heparan sulfate releases VEGF and FGF-2, which signal ERK phosphorylation and cause pro-inflammatory cytokine induction. Production of pro-inflammatory factors (IL-6, MMP-9, FGF-2, HGF) then contributes to inflammation and infiltration of macrophages, T cells, and Nk cells in the cornea. In addition, HSV-1-infected corneas predominantly produce VEGF-A that leads to angiogenic sprouting