Figure 10. Chronic midazolam administration decreases the capacity of tau to bind to taxol-stabilized preformed microtubules in hTau mice.
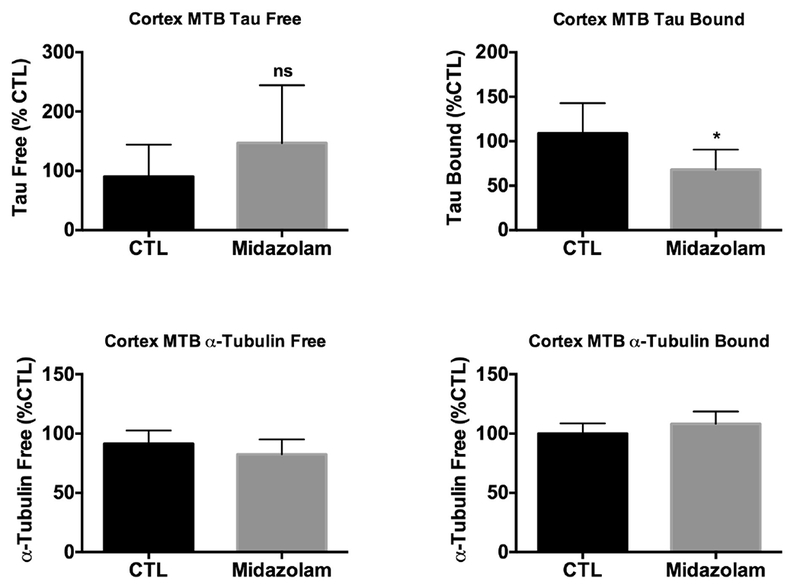
Neocortical brain proteins from 7-month-old hTau mice treated midazolam 5 mg/kg/h or 0.9% saline (n = 6 per group) for 24h were extracted and incubated with taxol-stabilized microtubules. Total tau and μ-tubulin levels from the microtubule free and bound fractions were evaluated by immunoblot analysis. Levels of total tau and μ-tubulin in microtubule free (A,C, respectively) and bound fractions (B,D, respectively) following midazolam treatment were compared to saline (Ctl) after controlling for gel loading with β-actin. Relative immunoreactive band intensities are expressed as a percent of Ctl and, for each condition, 2 representative immunoblot bands are displayed. Data are expressed as mean ± SD and * denotes P < 0.05 vs. Ctl using an unpaired t-test.
