Figure 9. Chronic midazolam administration increases hippocampal tau phosphorylation in hTau mice without altering tau solubility.
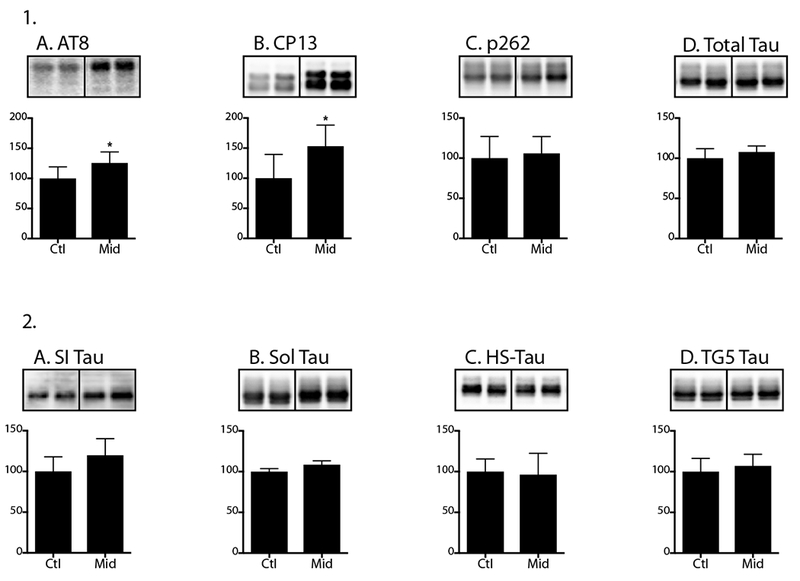
Hippocampal tau phosphorylation (% Ctl) at the AT8, CP13, and PHF-1 phosphoepitopes (1A-C) in 7-month-old hTau mice treated midazolam 5 mg/kg/h or 0.9% saline (n = 6 per group) and sacrificed 24h after the start of the chronic infusion. Normothermia was maintained throughout the study and rectal temperatures were similar at the time of hippocampal tissue harvest: Ctl 37.3 ± 1.0 °C and Midazolam 36.9 ± 0.3 °C. Phosphorylated tau levels were normalized to total tau (1D), after controlling for gel loading with β-actin. Levels of tau in the sarkosyl-insoluble (SI; 2A), sarkosyl-soluble (Sol; 2B), and heat-stabilized (HS; 2C) and total (TG5) fractions (2D) in cortical homogenates were measured using immunoblotting and total tau (TG5) antibody. Relative immunoreactive band intensities are expressed as a percent of Ctl and are displayed for each phosphoepitope and total tau. For each condition, 2 representative immunoblot bands are displayed. Data are expressed as mean ± SD and * denotes P < 0.05 vs. Ctl using an unpaired t-test.
