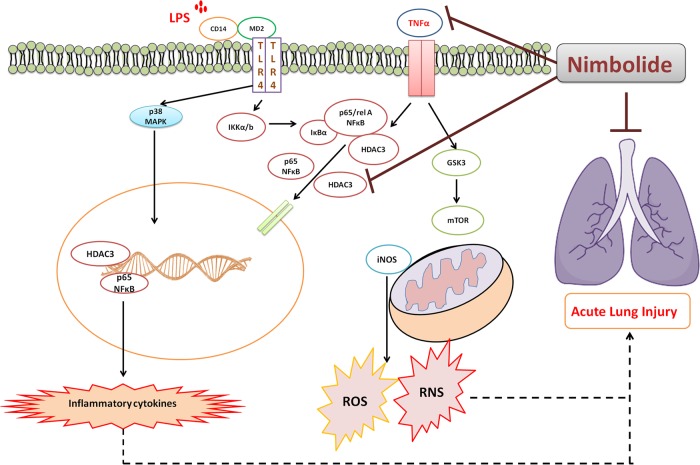
Fig. 8. Amelioration of LPS-induced alveolar inflammation by nimbolide.
A schematic diagram represents the molecular mechanism of nimbolide in LPS-induced ARDS. The bacterial endotoxin, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binds to its cognate toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) and the co-receptor cluster of differentiation 14 (CD14), which results in neutrophil accumulation, elevated vascular permeability, provocation of pulmonary edema. Nimbolide suppresses the nuclear translocation of NF-κB and HDAC-3. RNS- and ROS-induced ARDS is prevented by nimbolide by different canonical pathways