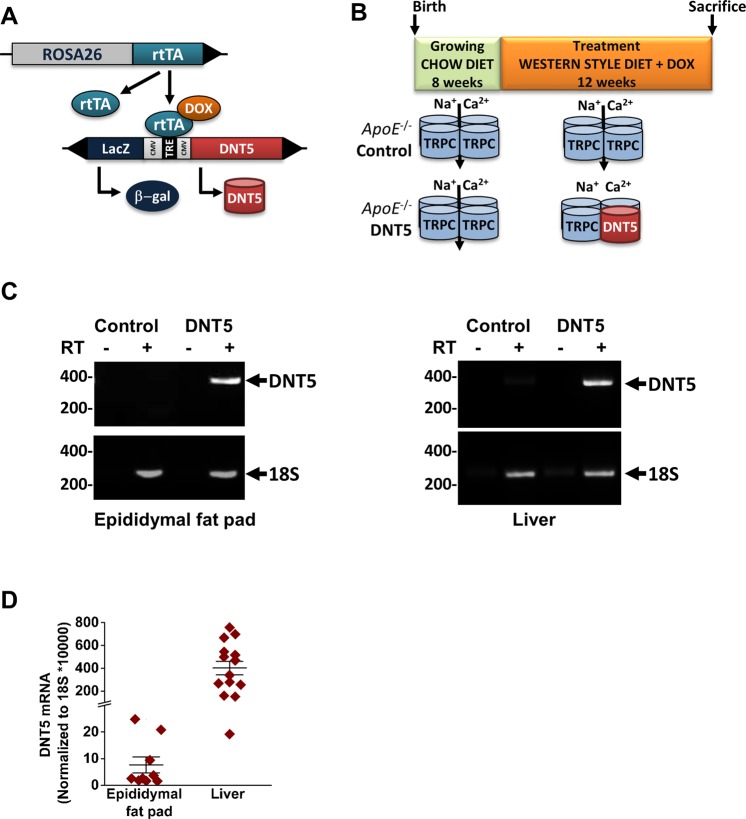
Figure 1.
Expression of DNT5 in hypercholesterolaemic mice. (A) Schematic of the transgenes regulating the expression of DNT5. DNT5 coding sequence was placed under the control of a Tetracycline Response Element (TRE) that co-regulated the expression of a LacZ reporter. Expression was dependent on the expression of a transactivator (rtTA) from the ROSA26 locus that conferred putatively global expression regulated in a time-controlled manner by addition of doxycycline (DOX) in the drinking water. Only mice with both transgenes expressed DNT5 and were referred as DNT5; non-and single-transgenic mice were the Controls. (B) Control and DNT5-expressing mice on ApoE−/− background were kept on standard chow diet and did not express DNT5 until 8 weeks of age. During the treatment phase (12 weeks), chow diet was replaced with western-style diet and DOX was given to mice of the two groups, triggering the expression of DNT5 in DNT5 group but not in Controls. All data were from mice which had been provided with western-style diet and DOX for 12 weeks. (C) Gel-electrophoresis of end-point RT-PCR performed on epididymial fat pad (left) and liver (right). Results are shown without (−) and with (+) reverse transcription (RT). The sizes of the DNA markers is indicated on the left in base-pairs. The arrows point to the expected PCR product sizes. DNT5 mRNA was detected in tissues from DOX-treated double transgenic mice but not Controls. Gels were cropped for presentation purposes. Full length gels are presented in Supplementary File 1. (D) Real-time PCR analysis of the expression of DNT5 mRNA in the epididymal fat pad (N = 9) and liver (N = 14) of DOX-treated double transgenic mice (DNT5 group).