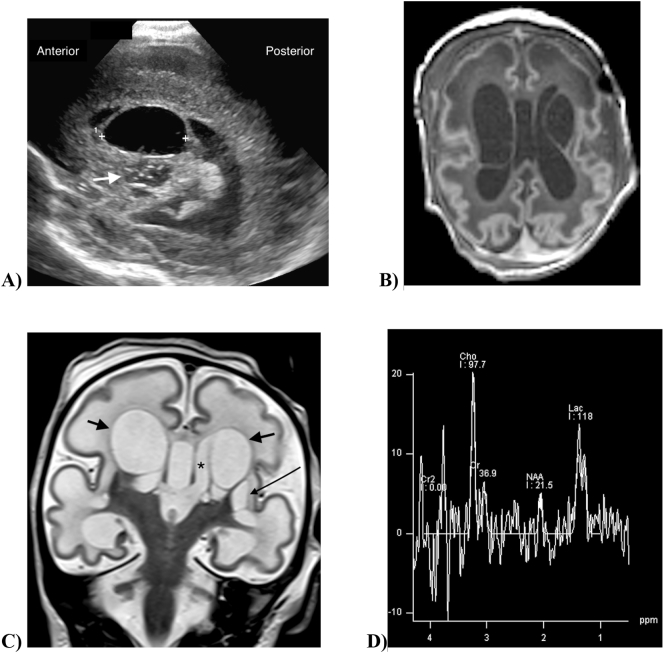
Fig. 1.
Neuroimaging in an infant with FOXRED1-related complex 1 deficiency and cerebral cysts. 1A) Cranial ultrasound on the first day of life. Parasagittal image in the plane of the left lateral ventricle shows a large cyst (markers) invaginating into the lateral ventricle. Bubbly cystic change is seen in the basal ganglia inferior to the cyst (arrow). 1B) Axial T1-weighted MR scan at 13 days of age shows large bilateral periventricular cysts. There is diffusely reduced gyral complexity with shallow sulci, most marked in the frontal lobes. The periventricular and subcortical white matter is diffusely T1-hypointense. 1C) Coronal T2-weighted MR scan shows bilateral periventricular cysts (short arrows) adjacent to the lateral ventricles (asterisk). Small cysts are present in the left basal ganglia (long arrow). The sylvian fissures and cerebral cortex are simple, and there is diffuse T2-hyperintensity of the white matter including the corpus callosum. 1D) Single voxel MR spectroscopy at TE288 in the right basal ganglia shows increased brain lactate with a lactate doublet at 1.3 ppm, and markedly diminished NAA (N-acetyl aspartic acid).