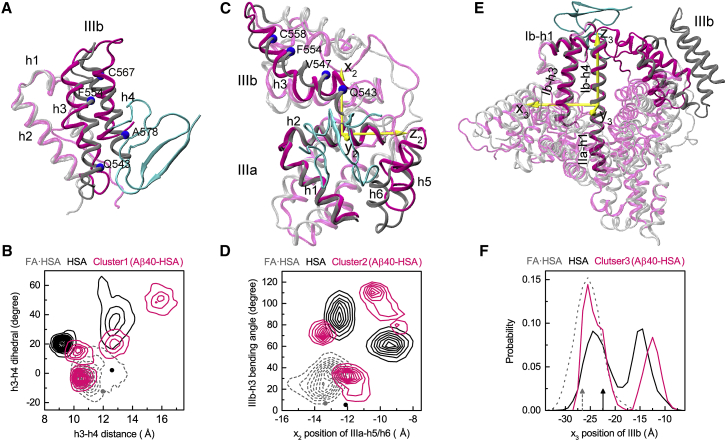
Figure 6.
Conformational changes of apo HSA accompanying Aβ40 binding to the three major sites. (A), (C), and (E) show the superposition of HSA in the representative poses (magenta) with the FA·HSA crystal structure (gray); Aβ40 is in cyan. (B), (D), and (F) show quantitative measurements of structural differences among Aβ40-bound, apo, and FA·HSA. In (B), the distance and relative tilt angle between the subdomain IIIb h3 and h4 helices are measured. The latter is defined as the dihedral formed by the Cα atoms of Q543, F554, C567, and A578. Dark and gray dots indicate values in the crystal structures. In (D), the movement of IIIa-h5/h6 relative to IIIa-h2 and the bending angle of IIIb-h3 are measured. The former is according to the position of IIIa-h5/h6 along the x2 axis, which is perpendicular to the helical axis of IIIa-h2 and points toward IIIb. The latter is defined as the angle between two vectors, one connecting Q543–V547 and the other connecting F554–C558. Dark and gray dots indicate values in the crystal structures. In (F), the movement of IIIb relative to the long helix connecting Ib-h4 and IIa-h1 is measured, as measured by the IIIb center of mass along the x3 axis. The latter is perpendicular to the helical axis of the long helix and points toward IIa-h3. Black and gray rrowsa indicate values in the crystal structures. To see this figure in color, go online.