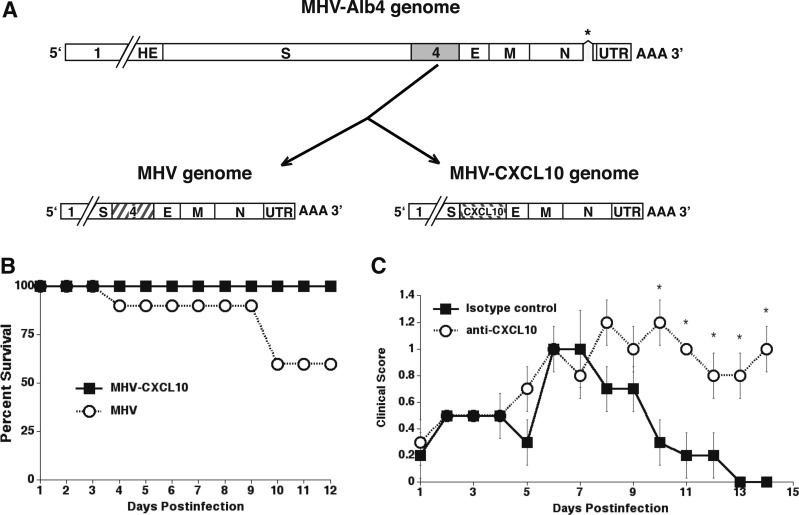
FIG. 5.
MHV-CXCL10 and MHV have genetic similarity. Both viruses were generated by a recombination reaction with the thermolabile N gene deletion (designated by asterisk) mutant MHV-Alb4 and mRNA generated from a transcription reaction using plasmids that encode from upstream of gene 4 to the 3′ end of MHV-CXCL10 and MHV. (A) The recombination reaction for MHV results in a recombinant that is genetically identical with the WT virus. MHV-CXCL10 is identical with MHV except that gene 4 is replaced by the coding sequence for CXCL10. (B) CXCL10−/− mice i.c. infected with MHV-CXCL10 exhibit 100% survival, whereas only 60% of MHV-infected mice survive to day 12 p.i. (C) Treatment of MHV-CXCL10-infected mice with an anti-CXCL10-neutralizing Ab results in significantly increased (*p ≤ 0.05) clinical scores compared with treatment with an isotype control Ab (data shown are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean) (89). E, E protein (small envelope protein); HE, hemagglutinin-esterase; M, membrane protein; N, nucleocapsid protein; S, surface protein; UTR, 3′ untranslated region; WT, wild type.