Figure 7.
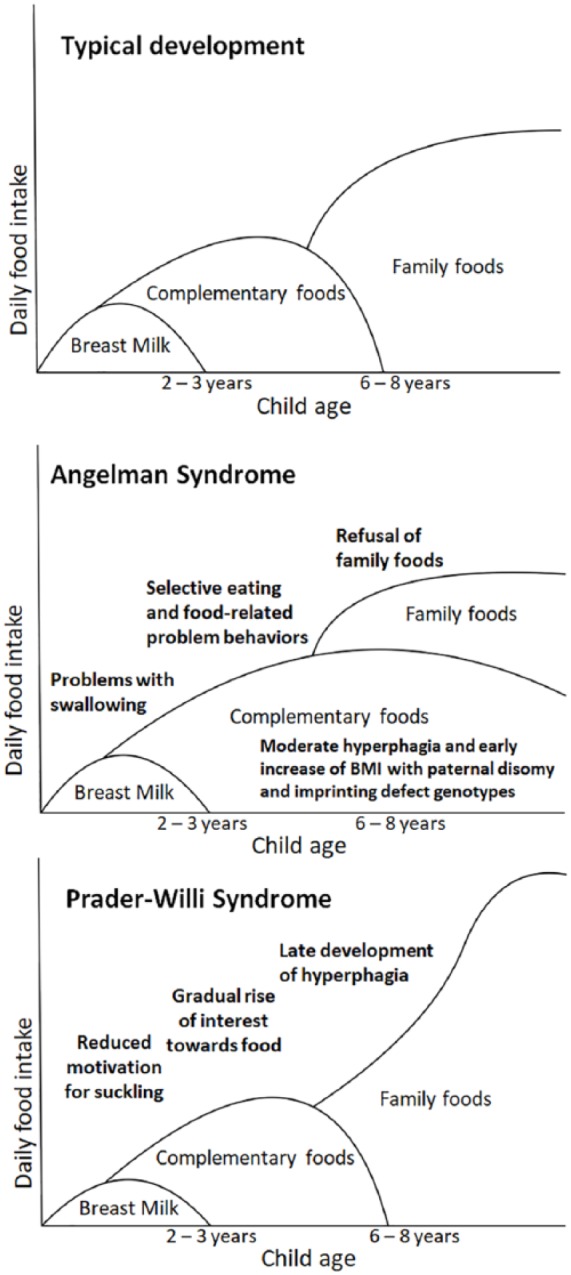
The development food preferences and hyperphagia in AS and PWS as compared to typical childhood development. Maternally provided breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for the infant until the age of weaning at the age of 2–3 years, while specially prepared complementary foods are gradually introduced from the age of 6 months and onwards. Diverse family foods resembling an adult diet replace complementary foods by the age of 6–8 years. Poor feeding during infancy is prominent in both AS and PWS, although for different reasons. A gradual rise of interest toward food and late development of hyperphagia can be seen in PWS, whereas AS may involve comparably earlier development of hyperphagia and a specific interest for complementary foods and prolonged refusal of family foods.
