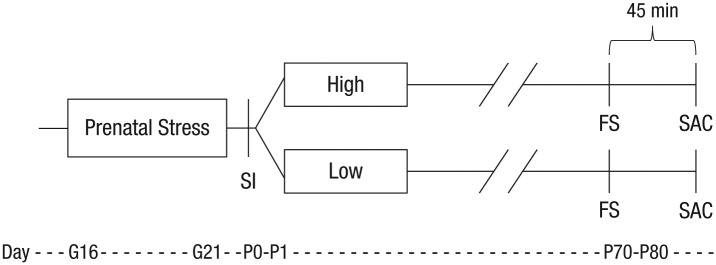
Fig. 1.
Experimental design. Pregnant voles assigned to the prenatal-stress condition were exposed to a social stressor 10 min per day for the last 5 days of gestation (G16–G21). Within 24 hr of birth (P0–P1), voles were subject to a social-isolation (SI) test and then cross-fostered to either high- or low-contact parents for the rearing condition. During adulthood (P70–80), subjects underwent a forced swim (FS) test to measure anxietylike behavior and were sacrificed (SAC) 45 min later to collect plasma and brains. The procedure for subjects in the control groups is not illustrated, but these subjects were similarly cross-fostered to either high- or low-contact parents and underwent all procedures (with the exception of prenatal stress) in the same timeline. G = gestational day; P = postnatal day; P0 = day of birth.