Figure 5.
HMGB1 Blockade Inhibits Endothelial Cell Activation after oHSVtreatment In Vitro and In Vivo
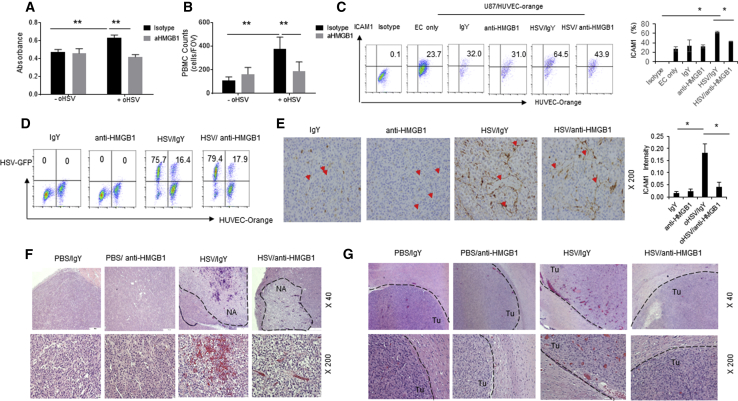
(A) Impact of HSVQ-released HMGB1 on vascular permeability was measured by the ability of Evans blue albumin to permeate through a monolayer of primary HUVEC cells. Monolayer of confluent HUVECs was seeded in the upper chamber of a boyden chamber, and the cells were treated with conditioned medium from infected glioma cell in the presence or absence of HMGB1-blocking antibody. Data shown are mean spectrophotometric quantitation of Evans blue dye that permeated through the monolayer. (B) Fluorescently labeled human donor PBMCs were incubated with HUVEC monolayer treated with conditioned medium from infected glioma cells in the presence or absence of HMGB1-blocking antibodies for 1 hr, and then unbound PBMCs were washed away. The number of PBMCs adhered to endothelial cells was quantified by measuring fluorescence. Data shown are mean fluorescence ± SD. (C and D) HSVQ-infected U87ΔEGFR cells were co-cultured with endothelial cells labeled with cell-tracker orange (HUVEC-orange) for 24 hr. U87ΔEGFR cells were infected with or without oHSV for 1 hr and overlaid with HUVEC-orange cells treated with isotype control or HMGB1-blocking antibody. After 24 hr co-culture, cells were stained with ICAM1 antibody and the effect of HMGB1 neutralization on ICAM1 expression and oHSV replication is analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative dot plots for ICAM1 expression from one of three independent experiments is shown. Mean of three independent experiments ± SD is shown on the right. (D) Dot blots of GFP-positive-infected cells with or without HMGB1 blockade. (E) Photomicropgraphs and quantification of intensity of IHC staining of ICAM1 expression in U87ΔEGFR xenografts in nude mice. In brief, mice with subcutaneous U87ΔEGFR xenografts were treated with HSVQ (1 × 105 pfu) or PBS when tumors reached 150–200 mm3. Mice were also treated with or without HMGB1-blocking antibody, 1 day after virus treatment. Two days post-virus-treatment, mice were euthanized, and harvested tumor sections were stained for ICAM1 (red arrowheads). Quantification of ICAM1 intensity was analyzed by ImageJ software (*p < 0.05 for oHSV + anti-HMGB1 versus oHSV + IgY, IgY, anti-HMGB1) (n = 3 mice/group and 10 images/section). (F and G) Photomicrographs of H&E staining of subcutaneous U87ΔEGFR xenograft tumor (F) or intracranial GBM12 xenograft tumor sections (G). Mice with tumors were treated with an intratumoral injection of 5 × 105 pfu HSVQ/PBS with or without HMGB1 blockade as described above. Black dashed lines indicated tumor necrosis area (NA) after oHSV injection apparent in subcutaneous tumors. Black dashed line in (G) marks the interface between tumor (Tu) and normal brain tissue.