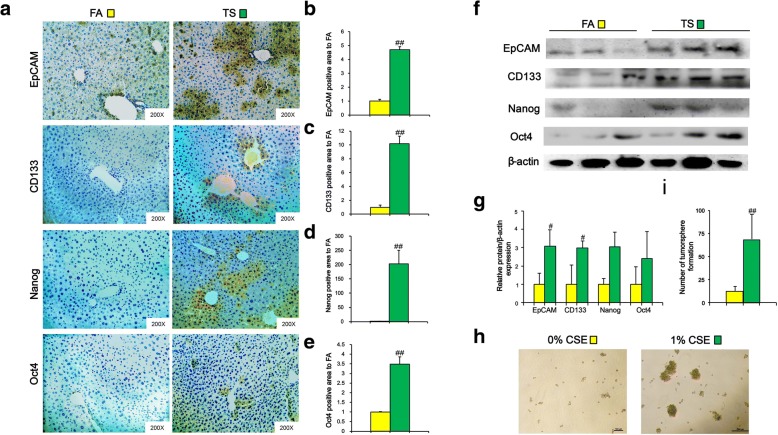
Fig. 1.
Long term TS exposure induced liver cells acquisition of CSC-like properties. Mice were exposed to TS for 12 weeks. The alternation of liver CSCs markers was analyzed by immunohistochemical staining (IHC) (a). EpCAM (b), CD133 (c), Nanog (d) and Oct4 (e)-positive areas in TS group relative to FA group. f Western blotting was used to analyze the expression of the indicated genes. g Densitometry results were shown as fold change compared with FA group after normalization to β-actin. Six animal samples per group were used for the densitometric analysis. h-i LO2 immortalized human liver cells were exposed to 0% or 1% concentrations of cigarette smoke extract (CSE) for 14 days and then cultured with serum free medium for another 7 days. Images of tumorsphere (h) and the numbers of tumorsphere (i) were examined. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. The significance was assessed with unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, compared with FA control or 0% CSE. FA = filtered air; TS = tobacco smoke