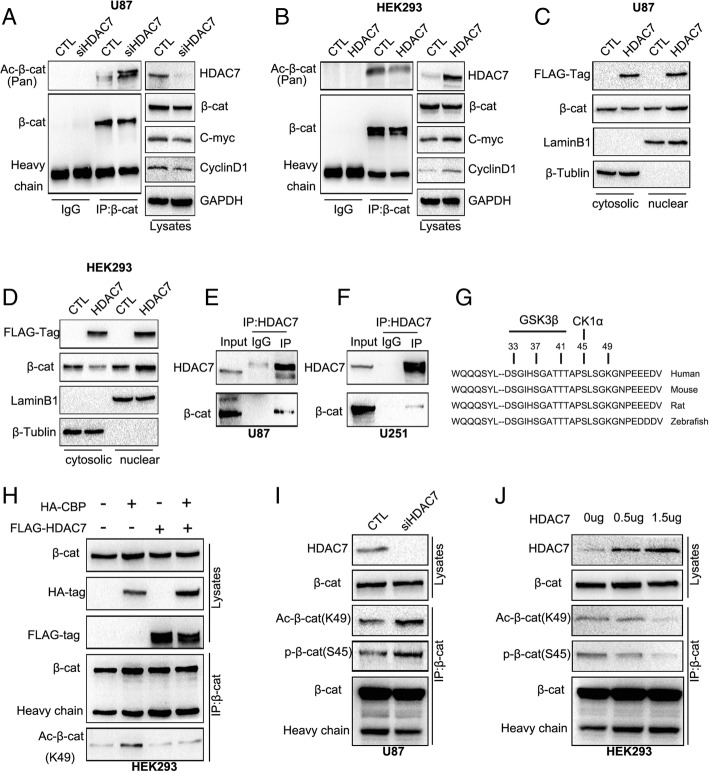
Fig. 5.
HDAC7 down-regulates the levels of β-catenin acetylation at Lys49 and phosphorylation at Ser45. a, b After transfection of siRNA-HDAC7 in U87 cells, the total acetylation level of β-catenin were upregulated and Wnt pathway target gene protein expression were downregulated, detected by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting (a). But after transfection of HDAC plasmid with HEK293, the opposite result was obtained (b). No significant changes in total β-catenin protein were observed when both overexpression and knockdown of HDAC7. GAPDH served as a loading control. c, d Cytosolic fractionation and immunofluorescence assays were applied to detect β-catenin nuclear import after transfection of HDAC7 plasmid in U87 (c) or HEK293 (d) cells, indicating transfection of HDAC7 promotes the β-catenin nuclear import. β-Tublin and LaminB1 were cytoplasmic and nucleus loading controls, respectively. e, f Interaction between endogenous HDAC7 and β-catenin in U87 and U251 glioma cells. Cell lysates from U87 (e) and U251 (f) cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HDAC7 antibody or control IgG and then examined for β-catenin expression by anti-β-catenin immunoblotting. g, h HDAC7 could reverse the up-regulation of β-catenin acetylation at Lys49 induced by CBP. Schematic diagram of β-catenin serine/threonine and lysine residues (g). The HA-CBP and FLAG-HDAC7 plasmids were co-transfected in HEK293 cells. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting assays were used to detect the acetylation level of β-catenin at Lys49. total β-catenin was the loading control (H). i, j After knockdown of HDAC7 in U87 cells, β-catenin acetylation level at Lys49 and phosphorylation level at Ser45 were significantly upregulated (i), With the increase of HDAC7 plasmid concentration, the level of β-catenin acetylation and phosphorylation gradually decreased (j). the total β-catenin level was the loading control