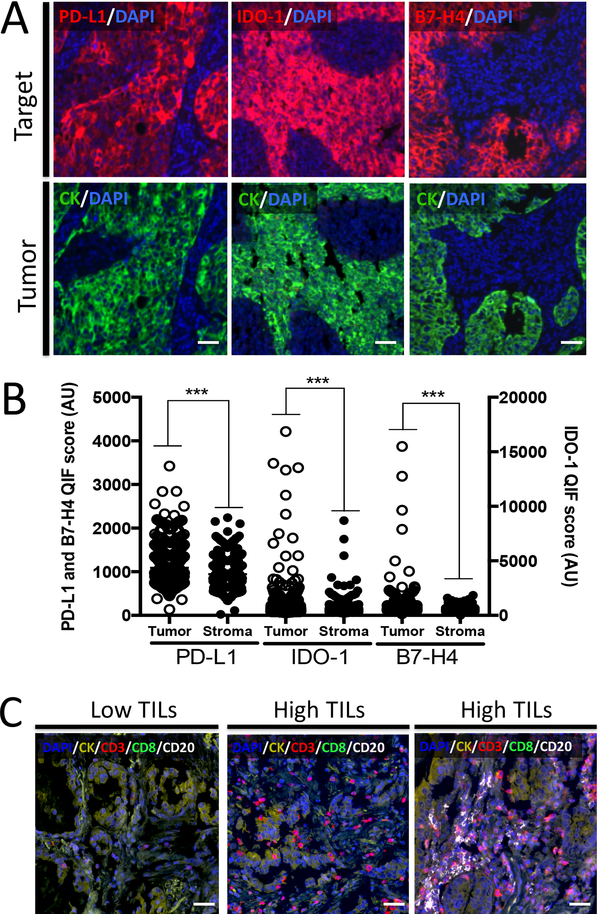
Figure 1. Detection of PD-L1, IDO-1, B7-H4 and TIL subsets using multiplex quantitative immunofluorescence (QIF) in lung cancer.
A) Representative fluorescence images showing the simultaneous detection of PD-L1, IDO-1 or B7-H4 (red fluorescence channel) and cytokeratin (green channel) in lung cancer samples using QIF. The upper panel shows tumors that are positive for each of the markers and the lower panel shows the cytokeratin positivity in the same samples. The target protein is indicated with red colored text in each figure. Green indicates the cytokeratin positive compartment and blue designated the DAPI positive nuclei. B) Levels of PD-L1, IDO-1 and B7-H4 in the tumor and stromal compartment of lung carcinomas from the studied cohorts. Each dot indicates the QIF level of the marker in a different tumor sample. ***=P<0.001. C) Representative fluorescence images showing the detection of TIL subsets in lung cancer samples by simultaneous staining of DAPI, cytokeratin (CK, yellow channel), CD3 (red channel), CD8 (green channel) and CD20 (white channel). Cases with low TILs (left panel), high TILs with predominant CD3+ T-cells (center panel) and with high CD3 and CD20+ B lymphocytes (right panel) are presented. Bar=100 μm.