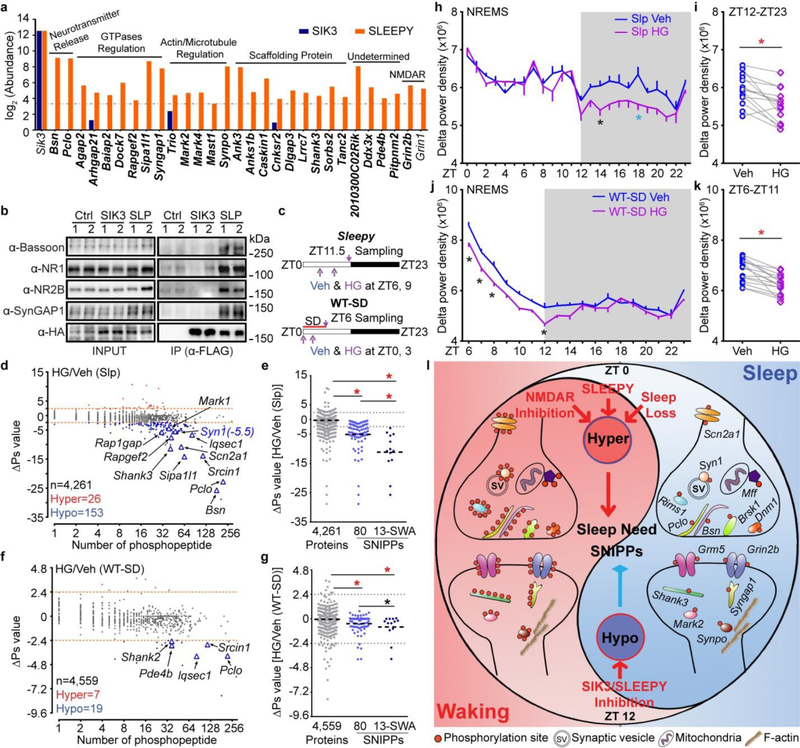
Figure 4 |. SLEEPY preferentially interacts with SNIPPs and alters sleep-wake homeostasis.
a, Comparison of mass-spec signals of SNIPPs in immunoprecipitates of SLEEPY and SIK3. b, IP-Western validates SLEEPY-SNIPPs interaction (two independent experiments). c, A schematic of SIK3 inhibition in Sleepy (Slp) and sleep-deprived wild-type (WT-SD) mice. d-g, Global (d, f) and quantitative (e, g) ∆Ps analysis of HG/Veh (Slp) and HG/Veh (WT-SD) groups. h-k Circadian (h, j) and mean (i, k) absolute NREMS delta power analysis of HG/Veh (Slp) (n = 14) and HG/Veh (WT-SD) (n = 16) groups. l, A molecular model of synaptic homeostasis and sleep-wake homeostasis. Mean, one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s (e, g); Mean ± s.e.m., two-way ANOVA, Sidak’s (h, j); Paired t-test, two-tailed (i, k). *(black) P < 0.05; *(cyan) P < 0.01; *(red) P < 0.001.