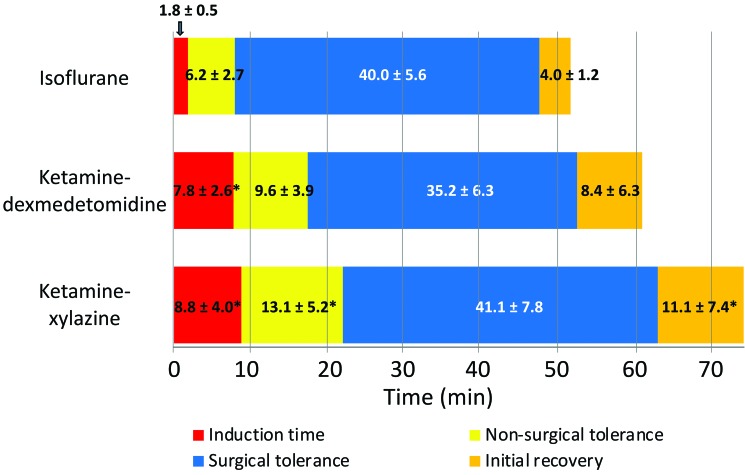
Figure 1.
Duration of the anesthesia stages due to isoflurane, ketamine–dexmedetomidine, and ketamine–xylazine. Compared with ketamine–dexmedetomidine or ketamine–xylazine, isoflurane produced a shorter induction time and more rapid entry into the surgical tolerance phase of anesthesia. At 35 to 40 min after induction, isoflurane was withdrawn by removing the nose cone, and ketamine–dexmedetomidine and ketamine–xylazine anesthesia were partially reversed by injecting atipamezole to block the effects of dexmedetomidine and xylazine. Isoflurane produced approximately 2-fold and 2.5-fold shorter time to initial recovery compared with ketamine–dexmedetomidine and ketamine–xylazine, respectively. Values are given as mean ± 1 SD; *, value significantly different (P < 0.05) from that for isoflurane-treated rats. Data were analyzed by using ANOVA; a P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.