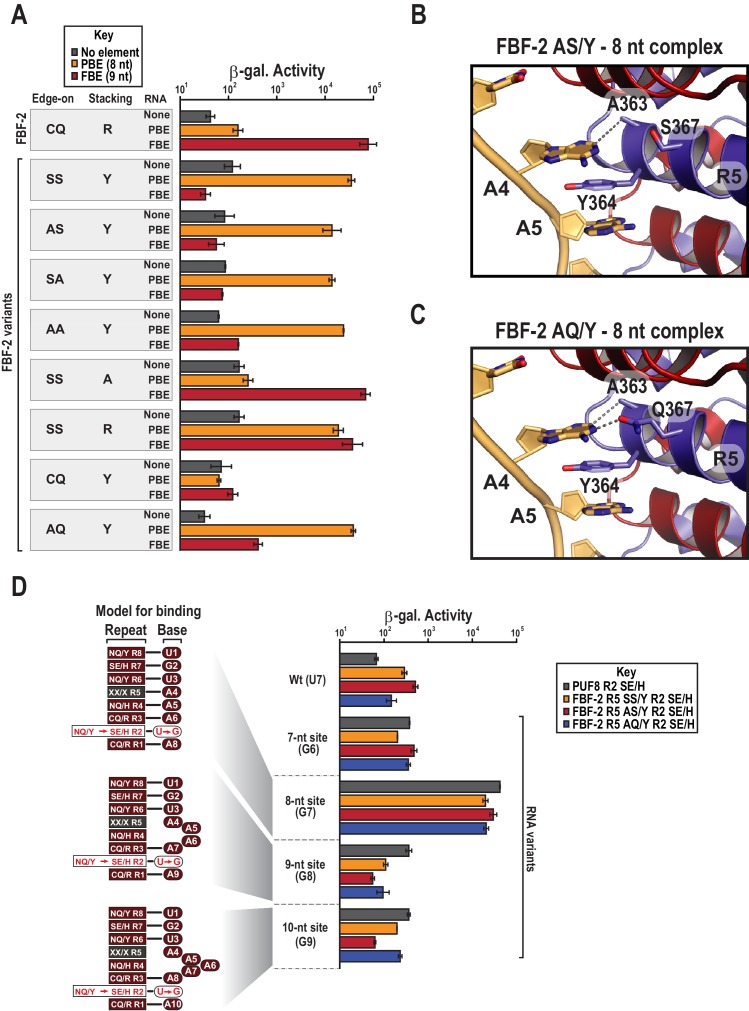
Figure 4. Y364 in the FBF-2 SS/Y variant is critical for 8-nt PBE selectivity.
(A) Interaction of FBF-2 TRM variants with 8-nt PBE and 9-nt FBE RNAs. Yeast 3-hybrid analyses of binding by FBF-2 WT and the FBF-2 SS/Y variant to an MS2 hairpin (None, grey) or an MS2 hairpin fused to an 8-nt PBE (orange) or a 9-nt FBE (red). Binding activity is shown as units of β-galactosidase activity. Source data areavailable in Figure 4—source data 1. (B) The FBF-2 AS/Y variant binds to the PBE RNA in a 1:1 recognition pattern similar to the SS/Y variant. Hydrogen bond and van der Waals interactions are indicated with dashes. (C) The FBF-2 AQ/Y variant binds to the PBE RNA in a 1:1 recognition pattern. (D) The FBF-2 variants retain recognition of the 3´ sequence. Yeast 3-hybrid analyses of binding by PUF-8 and FBF-2 variants to an MS2 hairpin fused to an 8-nt WT PBE or a 7–10-nt PBE with the penultimate nucleotide changed to G. Binding activity is shown as units of β-galactosidase activity normalized to cell count. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of three replicate measurements. Mutants in PUF-8, FBF-2 SS/Y, FBF-2 AS/Y, or FBF-2 AQ/Y introduce a requirement for a G base opposite repeat R2, and interaction with only 8-nt sequences indicates the importance of the 3´ sequence. Source data areavailable in Figure 4—source data 2.
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays.
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. The FBF-2 R5 CQ/Y mutant is expressed in yeast.