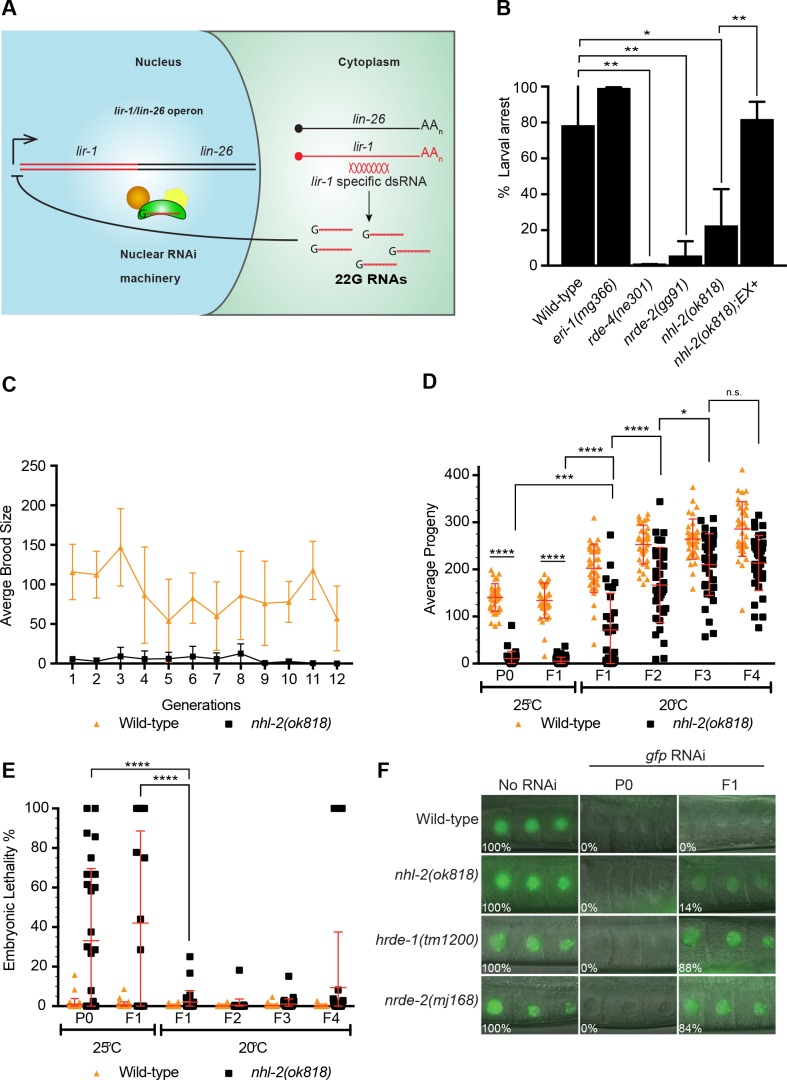
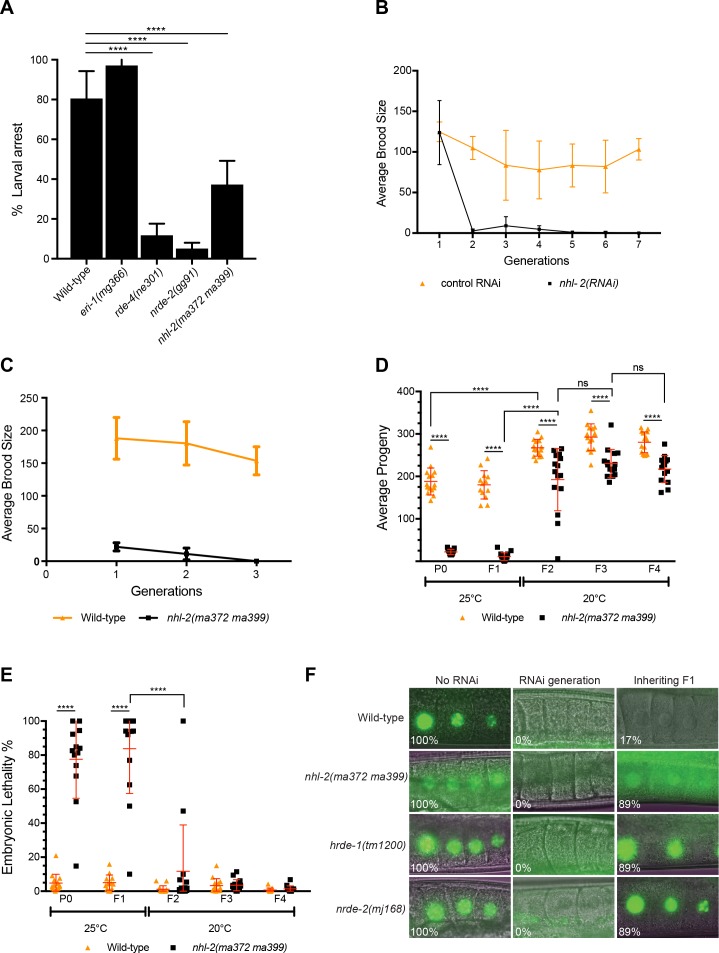
Figure 3. Analysis of nuclear RNAi pathways in nhl-2(ok818) mutants.
(A) The nuclear RNAi pathway silences somatic targets. dsRNA targeting the lir-1 mRNA leads to the generation of 22G small RNAs in the cytoplasm and the nuclear RNAi pathway uses these 22G RNAs to target the endogenous lir-1/let-26 locus for silencing. (B) nhl-2(ok818) worms are resistant to lir-1 RNAi. This phenotype was rescued in transgenic nhl-2(ok818) worms expressing an GFP-NHL-2 extrachromosomal array (Ex+) under control of the putative nhl-2 promoter. Percent larval arrest represents mean of two biological replicates ±SD; **=P values <0.001, *=P values <0.0418, n > 100. (C) nhl-2(ok818) worms display a mortal germline phenotype at 25°C. Error bars indicate mean ±SD, n = 6. (D) Analysis of transgenerational brood size and embryonic lethality (E) of wild-type and nhl-2(ok818) worms. ****=P values <0.0001, ***=P values <0.0004, *=P values <0.0418. Error bars indicate mean ±SD, n = 37. (F) nhl-2(ok818) worms have a minor defect in RNAi inheritance at 20°C. Transgenic worms of the indicated genotypes expressing pie-1::gfp::h2b were fed gfp RNAi for one generation and then grown on OP50 thereafter. Animals were scored for GFP expression using a fluorescence microscope at 63X objective. The percentage of animals expressing GFP is shown, n ≥ 37. Germlines of nhl-2(ok818) worms grown at 25°C were unable to be scored due to the disorganised nature of the proximal gonad.